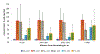Metal contamination in environmental media in residential areas around Romanian mining sites
- PMID: 27930368
- PMCID: PMC7385540
- DOI: 10.1515/reveh-2016-0033
Metal contamination in environmental media in residential areas around Romanian mining sites
Abstract
Hard-rock mining for metals, such as gold, silver, copper, zinc, iron and others, is recognized to have a significant impact on the environmental media, soil and water, in particular. Toxic contaminants released from mine waste to surface water and groundwater is the primary concern, but human exposure to soil contaminants either directly, via inhalation of airborne dust particles, or indirectly, via food chain (ingestion of animal products and/or vegetables grown in contaminated areas), is also, significant. In this research, we analyzed data collected in 2007, as part of a larger environmental study performed in the Rosia Montana area in Transylvania, to provide the Romanian governmental authorities with data on the levels of metal contamination in environmental media from this historical mining area. The data were also considered in policy decision to address mining-related environmental concerns in the area. We examined soil and water data collected from residential areas near the mining sites to determine relationships among metals analyzed in these different environmental media, using the correlation procedure in the SAS statistical software. Results for residential soil and water analysis indicate that the average values for arsenic (As) (85 mg/kg), cadmium (Cd) (3.2 mg/kg), mercury (Hg) (2.3 mg/kg) and lead (Pb) (92 mg/kg) exceeded the Romanian regulatory exposure levels [the intervention thresholds for residential soil in case of As (25 mg/kg) and Hg (2 mg/kg), and the alert thresholds in case of Pb (50 mg/kg) and Cd (3 mg/kg)]. Average metal concentrations in drinking water did not exceed the maximum contaminant level (MCL) imposed by the Romanian legislation, but high metal concentrations were found in surface water from Rosia creek, downstream from the former mining area.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure assessment for the abandoned metal mine area contaminated by arsenic.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Dec;41(6):2443-2458. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00296-5. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 31016607 Free PMC article.
-
Contaminants in surface water and sediments near the Tynagh silver mine site, County Galway, Ireland.Sci Total Environ. 2015 Apr 15;512-513:261-272. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.026. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Sci Total Environ. 2015. PMID: 25634731
-
Traces of the past: assessing the impact of potentially toxic elements from an abandoned mine on groundwater and agricultural soil in San Luis Potosí, México.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 4;196(11):1015. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13081-4. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39365363
-
Sources, pathways, and relative risks of contaminants in surface water and groundwater: a perspective prepared for the Walkerton inquiry.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2002 Jan 11;65(1):1-142. doi: 10.1080/152873902753338572. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2002. PMID: 11809004 Review.
-
Shellfish and residual chemical contaminants: hazards, monitoring, and health risk assessment along French coasts.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011;213:55-111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21541848 Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to Environmental Organic Mercury and Impairments in Human Fertility.J Reprod Infertil. 2019 Jul-Sep;20(3):195-197. J Reprod Infertil. 2019. PMID: 31423423 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tamas CG. Endogenous breccias structures (breccia pipe–breccia dyke) and the petrometallogeny of Rosia Montana ore deposit (Metaliferi Mountains, Romania). Cluj-Napoca: Book of Science House, 2007:230pp.
-
- Navarro MC, Perez-Sirvent C, Martinez-Sanchez MJ, Vidal J, Tovar PJ, et al. Abandoned mine sites as a source of contamination by heavy metals: a case study in a semi-arid zone. J Geochem Explor 2008;96:183–93.
-
- Li Y, Wang Y, Gou X, Su Y, Wang G. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China. J Environ Sci 2006;18(6):1124–34. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang P, McBride MB, Xia H, Li N, Li Z. Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 2009;407(5):1551–61. - PubMed
-
- Lazar AL, Baciu C, Roba C, Dicu T, Pop C, et al. Impact of the past mining activity in Rosia Montana (Romania) on soil and vegetation. Environ Earth Sci 2014;72:4653–66.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials