The effects of hyaluronic acid on hemiplegic shoulder injury and pain in patients with subacute stroke: A randomized controlled pilot study
- PMID: 27930553
- PMCID: PMC5266025
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005547
The effects of hyaluronic acid on hemiplegic shoulder injury and pain in patients with subacute stroke: A randomized controlled pilot study
Abstract
Background: Hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP) is one of the most common comorbidities in stroke patients with flaccid shoulders. The pain limits functional motor recovery and affects the activities of daily living after acute stroke. This study investigated the effects of hyaluronic acid (HA) injection on pain reduction and motor function in subacute stroke patients with HSP and injury.
Methods: A randomized, double-blinded controlled trial was conducted in a medical center. Twenty-six subacute stroke patients were enrolled and randomly divided into 2 groups: the experimental group (n = 16) received ultrasound-guided, subacromial HA injections once per week for 3 weeks and conventional rehabilitation, whereas the control group (n = 10) received 0.9% sodium chloride injections once per week for 3 weeks and conventional rehabilitation. Shoulder pain and motor function were evaluated before and after the intervention using the visual analog scale (VAS) and the Fugl-Meyer assessment for the upper extremity (FMA-UE), respectively.
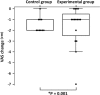
Results: In the experimental group, significant differences were found in VAS (P = 0.003), shoulder flexion (P = 0.03) and abduction (P = 0.02), and FMA-UE (P = 0.003) after treatment. In the control group, there were significant differences in VAS (P = 0.007), shoulder flexion (P = 0.035), and FMA-UE (P = 0.042) after treatment. The comparison of the changes in the parameters between the experimental and control groups, after each intervention, revealed a significant difference in VAS (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Subacromial HA injection could result in positive effects on shoulder pain and shoulder abduction in subacute stroke patients with HSP and injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Najenson T, Yacubovich E, Pikielni SS. Rotator cuff injury in shoulder joints of hemiplegic patients. Scand J Rehabil Med 1971;3:131–7. - PubMed
-
- Wanklyn P, Forster A, Young J. Hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP): natural history and investigation of associated features. Disabil Rehabil 1996;18:497–501. - PubMed
-
- Lindgren I, Jonsson AC, Norrving B, et al. Shoulder pain after stroke: a prospective population-based study. Stroke 2007;38:343–8. - PubMed
-
- Huang YC, Liang PJ, Pong YP, et al. Physical findings and sonography of hemiplegic shoulder in patients after acute stroke during rehabilitation. J Rehabil Med 2010;42:21–6. - PubMed
-
- Gamble GE, Barberan E, Bowsher D, et al. Post stroke shoulder pain: more common than previously realized. Eur J Pain 2000;4:313–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical