Constitutive activation of alternative nuclear factor kappa B pathway in canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma contributes to tumor cell survival and is a target of new adjuvant therapies
- PMID: 27931134
- PMCID: PMC6198319
- DOI: 10.1080/10428194.2016.1260122
Constitutive activation of alternative nuclear factor kappa B pathway in canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma contributes to tumor cell survival and is a target of new adjuvant therapies
Abstract
Activation of the classical nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) pathway is a common molecular event observed in both human and canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Although the oncogenic potential of the alternative NFκB pathway (ANFκBP) has also been recently identified in DLBCL, its precise role in tumor pathogenesis and potential as a treatment target is understudied. We hypothesized that up-regulation of the ANFκBP plays an important role in the proliferation and survival of canine DLBCL cells, and we demonstrate that the ANFκBP is constitutively active in primary canine DLBCL samples and a cell line (CLBL1). We further demonstrate that a small interfering RNA inhibits the activation of the NFκB pathway and induces apoptosis in canine DLBCL cells. In conclusion, the ANFκBP facilitates survival of canine DLBCL cells, and thus, dogs with spontaneous DLBCL can provide a useful large animal model to study therapies targeting the ANFκBP.
Keywords: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; alternative NFκB pathway; canine model; comparative pathology; targeting therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest:
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text of this article online at
Figures
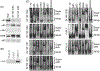
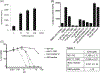
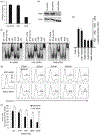
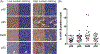
Similar articles
-
NEMO-binding domain peptide inhibits constitutive NF-κB activity and reduces tumor burden in a canine model of relapsed, refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jul 15;17(14):4661-71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3310. Epub 2011 May 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21610150 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive BR3 receptor signaling in diffuse, large B-cell lymphomas stabilizes nuclear factor-κB-inducing kinase while activating both canonical and alternative nuclear factor-κB pathways.Blood. 2011 Jan 6;117(1):200-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-290437. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Blood. 2011. PMID: 20889926 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib inhibits proteasomal degradation of IκBα and induces mitochondrial dependent apoptosis in activated B-cell diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Feb;55(2):415-24. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.806799. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 23697845
-
Rewired NFκB signaling as a potentially actionable feature of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Eur J Haematol. 2016 Dec;97(6):499-510. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12792. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Eur J Haematol. 2016. PMID: 27526684 Review.
-
Novel targeted therapies in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Semin Hematol. 2015 Apr;52(2):126-37. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Semin Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25805592 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypermethylation-Mediated Silencing of CIDEA, MAL and PCDH17 Tumour Suppressor Genes in Canine DLBCL: From Multi-Omics Analyses to Mechanistic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 5;23(7):4021. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074021. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409379 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profiling reveals common signatures of tumorigenesis and defines epigenetic prognostic subtypes of canine Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11724-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28912427 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide exploration of the methylome in aggressive B-cell lymphoma in Golden Retrievers reveals a conserved hypermethylome.Epigenetics. 2022 Dec;17(13):2022-2038. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2105033. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 35912844 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme is a new approach to treat canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Vet Comp Oncol. 2018 Dec;16(4):606-615. doi: 10.1111/vco.12428. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Vet Comp Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30101447 Free PMC article.
-
Improving human cancer therapy through the evaluation of pet dogs.Nat Rev Cancer. 2020 Dec;20(12):727-742. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0297-3. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32934365 Review.
References
-
- Swerdlow SHCE, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, et al. WHO classification of tumours of the haematopoietic and lymph-oid tissues. Lyon: IARC; 2008.
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations) [Internet]. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2012. Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/.
-
- Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Choi WW, et al. Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B-cell-like and non-germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4587–4594. - PubMed
-
- A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymph-oma. The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. Blood. 1997;89:3909–3918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
