Prediction of breast cancer risk based on common genetic variants in women of East Asian ancestry
- PMID: 27931260
- PMCID: PMC5146840
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0786-1
Prediction of breast cancer risk based on common genetic variants in women of East Asian ancestry
Abstract
Background: Approximately 100 common breast cancer susceptibility alleles have been identified in genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The utility of these variants in breast cancer risk prediction models has not been evaluated adequately in women of Asian ancestry.
Methods: We evaluated 88 breast cancer risk variants that were identified previously by GWAS in 11,760 cases and 11,612 controls of Asian ancestry. SNPs confirmed to be associated with breast cancer risk in Asian women were used to construct a polygenic risk score (PRS). The relative and absolute risks of breast cancer by the PRS percentiles were estimated based on the PRS distribution, and were used to stratify women into different levels of breast cancer risk.
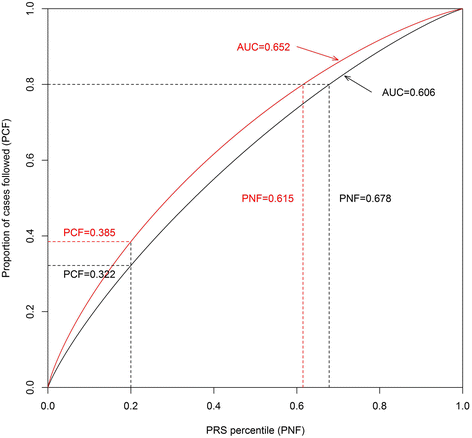
Results: We confirmed significant associations with breast cancer risk for SNPs in 44 of the 78 previously reported loci at P < 0.05. Compared with women in the middle quintile of the PRS, women in the top 1% group had a 2.70-fold elevated risk of breast cancer (95% CI: 2.15-3.40). The risk prediction model with the PRS had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.606. The lifetime risk of breast cancer for Shanghai Chinese women in the lowest and highest 1% of the PRS was 1.35% and 10.06%, respectively.
Conclusion: Approximately one-half of GWAS-identified breast cancer risk variants can be directly replicated in East Asian women. Collectively, common genetic variants are important predictors for breast cancer risk. Using common genetic variants for breast cancer could help identify women at high risk of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer risk; Methodology for SNP data analysis; Prediction model; Statistical methods in genetics.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA122756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C12292/A11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1281/A12014/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C5047/A10692/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA092585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 BC011118/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A8384/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A 10710/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA064277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118229/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C8197/A16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA137013/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical