Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation
- PMID: 27931262
- PMCID: PMC5146863
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0138-8
Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Jan 12;12(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0147-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28081701 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a major carrier of cholesterol and essential for synaptic plasticity. In brain, it's expressed by many cells but highly expressed by the choroid plexus and the predominant apolipoprotein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The role of apoE in the CSF is unclear. Recently, the glymphatic system was described as a clearance system whereby CSF and ISF (interstitial fluid) is exchanged via the peri-arterial space and convective flow of ISF clearance is mediated by aquaporin 4 (AQP4), a water channel. We reasoned that this system also serves to distribute essential molecules in CSF into brain. The aim was to establish whether apoE in CSF, secreted by the choroid plexus, is distributed into brain, and whether this distribution pattern was altered by sleep deprivation.
Methods: We used fluorescently labeled lipidated apoE isoforms, lenti-apoE3 delivered to the choroid plexus, immunohistochemistry to map apoE brain distribution, immunolabeled cells and proteins in brain, Western blot analysis and ELISA to determine apoE levels and radiolabeled molecules to quantify CSF inflow into brain and brain clearance in mice. Data were statistically analyzed using ANOVA or Student's t- test.
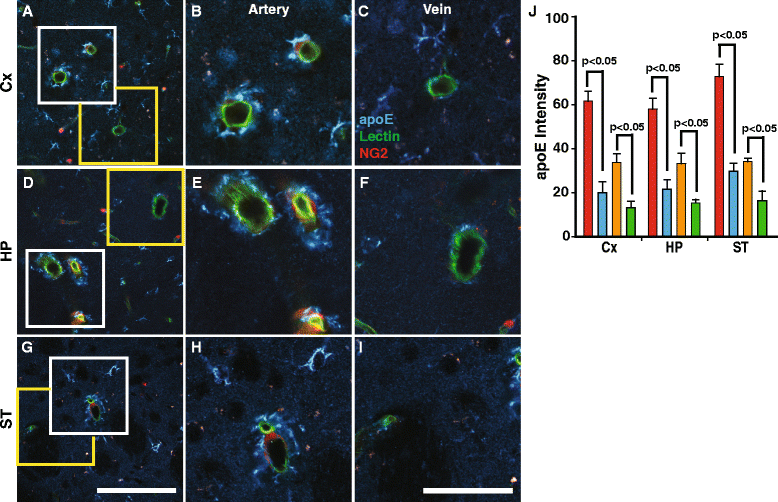
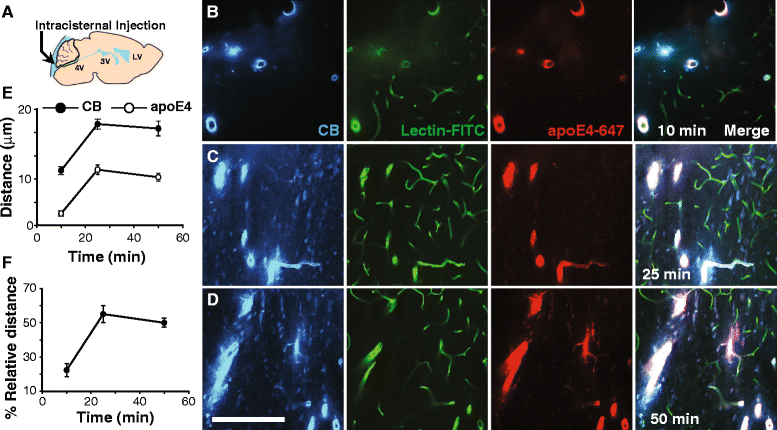
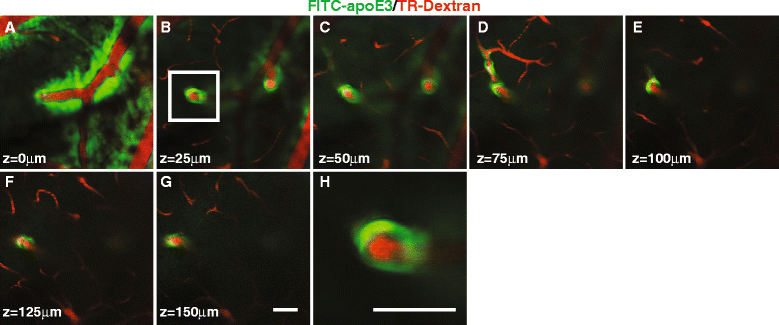
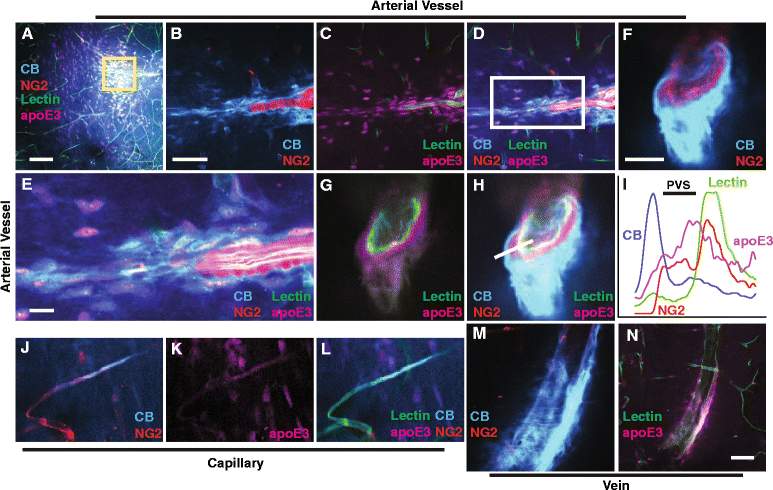
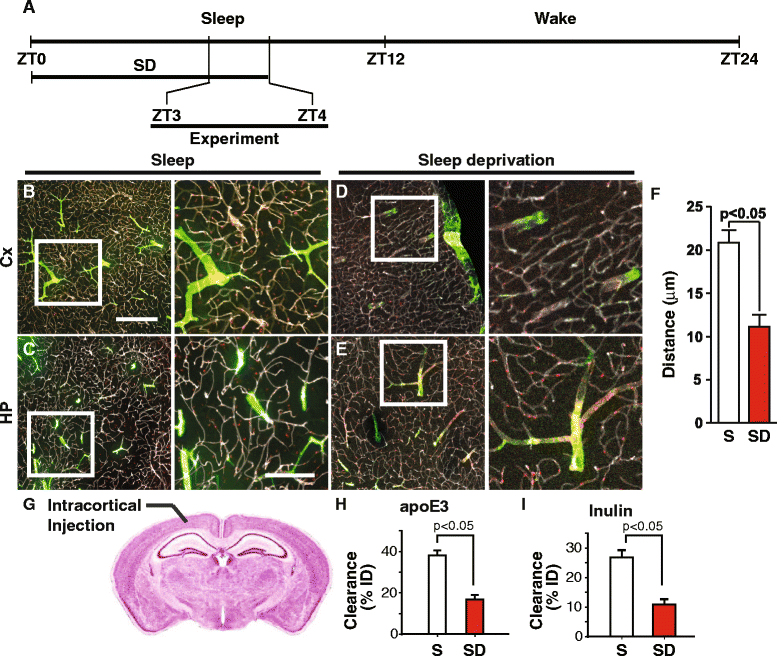
Results: We show that the glymphatic fluid transporting system contributes to the delivery of choroid plexus/CSF-derived human apoE to neurons. CSF-delivered human apoE entered brain via the perivascular space of penetrating arteries and flows radially around arteries, but not veins, in an isoform specific manner (apoE2 > apoE3 > apoE4). Flow of apoE around arteries was facilitated by AQP4, a characteristic feature of the glymphatic system. ApoE3, delivered by lentivirus to the choroid plexus and ependymal layer but not to the parenchymal cells, was present in the CSF, penetrating arteries and neurons. The inflow of CSF, which contains apoE, into brain and its clearance from the interstitium were severely suppressed by sleep deprivation compared to the sleep state.
Conclusions: Thus, choroid plexus/CSF provides an additional source of apoE and the glymphatic fluid transporting system delivers it to brain via the periarterial space. By implication, failure in this essential physiological role of the glymphatic fluid flow and ISF clearance may also contribute to apoE isoform-specific disorders in the long term.
Keywords: AQP4; Alzheimer’s disease; Brain clearance; Glymphatic pathways; Lymphatic system; Sleep/wake.
Figures
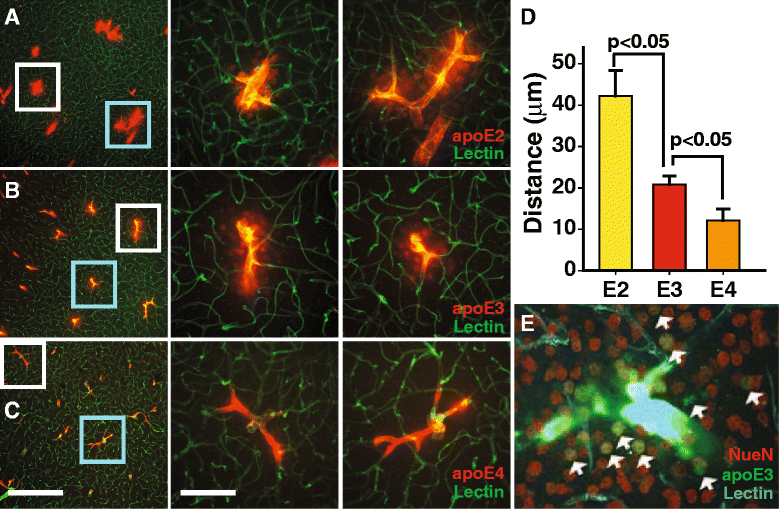
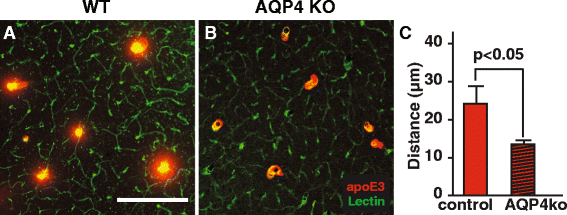
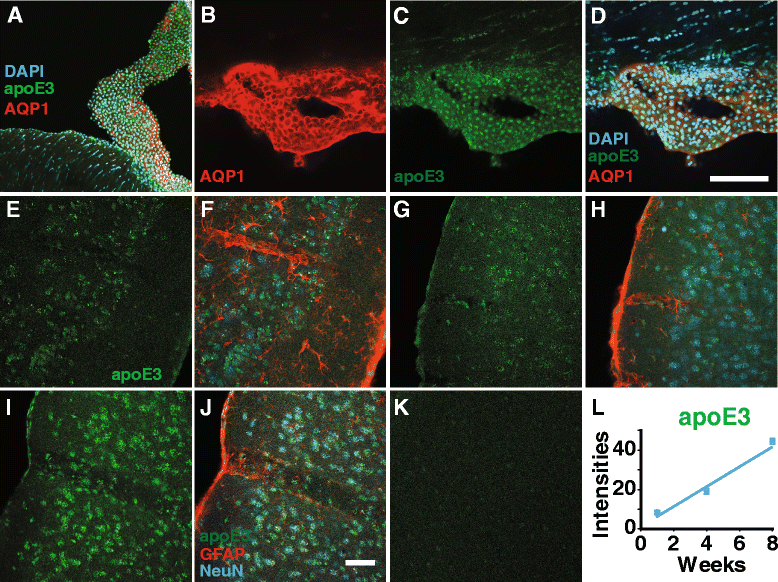
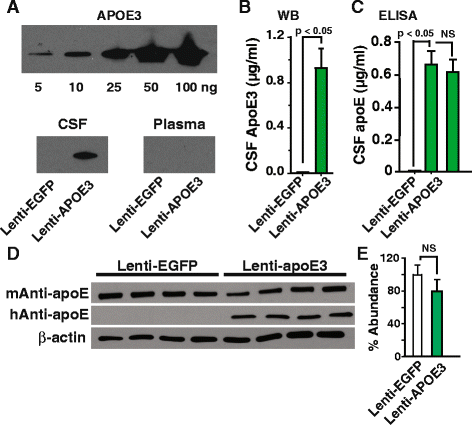

 - apoE;
- apoE;  - AQP4; There are many different types of apoE receptors, such as
- AQP4; There are many different types of apoE receptors, such as  - apoE receptor mainly on astrocyte and
- apoE receptor mainly on astrocyte and  - apoE receptor mainly on neuron
- apoE receptor mainly on neuronReferences
-
- Pitas RE, Boyles JK, Lee SH, Hui D, Weisgraber KH. Lipoproteins and their receptors in the central nervous system. Characterization of the lipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid and identification of apolipoprotein B, E(LDL) receptors in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:14352–14360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS090934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048769/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS078304/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT007945/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG047644/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG050212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS100366/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS086924/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS078167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS090934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

