Context-Dependent Role of Oxidized Lipids and Lipoproteins in Inflammation
- PMID: 27931771
- PMCID: PMC5253098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.11.002
Context-Dependent Role of Oxidized Lipids and Lipoproteins in Inflammation
Abstract
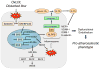
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL), which contains hundreds of different oxidized lipid molecules, is a hallmark of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. The same oxidized lipids found in OxLDL are also formed in apoptotic cells, and are present in tissues as well as in the circulation under pathological conditions. In many disease contexts, oxidized lipids constitute damage signals, or patterns, that activate pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) and significantly contribute to inflammation. Here, we review recent discoveries and emerging trends in the field of oxidized lipids and the regulation of inflammation, focusing on oxidation products of polyunsaturated fatty acids esterified into cholesteryl esters (CEs) and phospholipids (PLs). We also highlight context-dependent activation and biased agonism of Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) and the NLRP3 inflammasome, among other signaling pathways activated by oxidized lipids.
Keywords: inflammasome; inflammation; oxidized lipid; toll-like receptor.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Esterbauer H, et al. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11(1):81–128. - PubMed
-
- Miller YI, et al. Lipoprotein modification and macrophage uptake: Role of pathologic cholesterol transport in atherogenesis. Subcellular Biochemistry. 2010;51:229–251. - PubMed
-
- Tsimikas S, Miller YI. Oxidative modification of lipoproteins: Mechanisms, role in inflammation and potential clinical applications in cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:27–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

