The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3: Continued innovation for clinical trial improvement
- PMID: 27931796
- PMCID: PMC5536850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.10.006
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3: Continued innovation for clinical trial improvement
Abstract
Introduction: The overall goal of the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) is to validate biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease (AD) clinical trials. ADNI-3, which began on August 1, 2016, is a 5-year renewal of the current ADNI-2 study.
Methods: ADNI-3 will follow current and additional subjects with normal cognition, mild cognitive impairment, and AD using innovative technologies such as tau imaging, magnetic resonance imaging sequences for connectivity analyses, and a highly automated immunoassay platform and mass spectroscopy approach for cerebrospinal fluid biomarker analysis. A Systems Biology/pathway approach will be used to identify genetic factors for subject selection/enrichment. Amyloid positron emission tomography scanning will be standardized using the Centiloid method. The Brain Health Registry will help recruit subjects and monitor subject cognition.
Results: Multimodal analyses will provide insight into AD pathophysiology and disease progression.
Discussion: ADNI-3 will aim to inform AD treatment trials and facilitate development of AD disease-modifying treatments.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid phenotyping; Brain Health Registry; Centiloid method; Clinical trial biomarkers; Functional connectivity; Tau imaging.
Copyright © 2016 the Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dallas P. Veitch has no conflicts of interest to report.
Dr. Jack has provided consulting services for Eli Lily and owns stock in Johnson and Johnson.
Dr. Jagust consults for Genentech Inc., Banner Alzheimer Institute, Bioclinica, and Novartis
Dr. Petersen consults for Roche Inc., Merck Inc., Genetech Inc., and Biogen Inc.
Figures
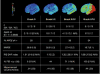
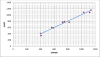
References
-
- Association As. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2016;12:459–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

