Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome - current perspectives
- PMID: 27932857
- PMCID: PMC5135404
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S94866
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome - current perspectives
Abstract
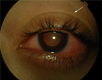
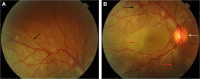
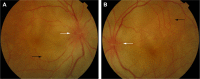
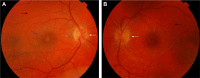
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome is a cause of noninfectious panuveitis, leading to significant vision loss in many patients. It is an autoimmune disease occurring in genetically susceptible individuals and clinically presents as bilateral panuveitis with serous retinal detachments and hyperemic, swollen optic discs, which are associated with neurological and auditory manifestations. Early diagnosis and prompt and adequate treatment with immunosuppressive agents (corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive drugs) may halt disease progression and prevent recurrences and vision loss. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the variable clinical aspects of this disease, highlighting diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Keywords: corticosteroid; multifocal choroiditis; panuveitis; serous retinal detachment; starry sky; sunset glow fundus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
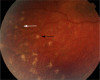
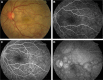
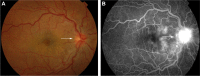
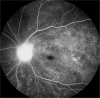
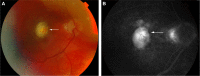
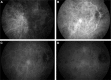
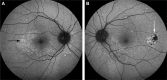
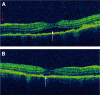
References
-
- Moorthy RS, Inomata H, Rao NA. Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 1995;39(4):265–292. - PubMed
-
- Read RW, Rechodouni A, Butani N, et al. Complications and prognostic factors in Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;131(5):599–606. - PubMed
-
- Yamaki K, Gocho K, Hayakawa K, Kondo I, Sakuragi S. Tyrosinase family proteins are antigens specific to Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease. J Immunol. 2000;165(12):7323–7329. - PubMed
-
- Sugita S, Takase H, Taguchi C, et al. Ocular infiltrating CD4+ T cells from patients with Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease recognize human melanocyte antigens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(6):2547–2554. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

