Mechanism of Nucleophilic Activation of (-)-Lomaiviticin A
- PMID: 27934014
- PMCID: PMC5339879
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b09657
Mechanism of Nucleophilic Activation of (-)-Lomaiviticin A
Abstract
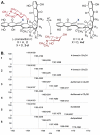
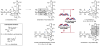
(-)-Lomaiviticin A (1) is a C2-symmetric cytotoxin that contains two diazofluorene functional groups and which induces double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. Evidence suggests DNA cleavage is initiated by hydrogen atom abstraction from the deoxyribose backbone. Here we demonstrate the formation of the vinyl radicals 1· and 2· from 1 by 1,7-addition of thiols to the diazofluorenes. These radicals can affect hydrogen atom abstraction from methanol and acetone. The first addition of thiol to 1 proceeds at a much greater rate than the second. The diazosulfide 5 formed en route to 1· has been detected at -50 °C and undergoes decomposition to 1· with a half-life of 110 min at -20 °C under air. These data, which constitute the first direct evidence for the generation of 1· and 2· from 1, provide insights into the mechanism of DNA cleavage by 1.
Figures
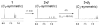



References
-
- He H, Ding WD, Bernan VS, Richardson AD, Ireland CM, Greenstein M, Ellestad GA, Carter GT. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:5362. - PubMed
- Woo CM, Beizer NE, Janso JE, Herzon SB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:15285. - PubMed
- Kersten RD, Lane AL, Nett M, Richter TKS, Duggan BM, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS. ChemBioChem. 2013;14:955. - PMC - PubMed
- Colis LC, Woo CM, Hegan DC, Li Z, Glazer PM, Herzon SB. Nat. Chem. 2014;6:504. - PMC - PubMed
- Colis LC, Hegan DC, Kaneko M, Glazer PM, Herzon SB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:5741. For a review, see. - PMC - PubMed
- Herzon SB, Woo CM. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012;29:87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

