An Ethenoadenine FAD Analog Accelerates UV Dimer Repair by DNA Photolyase
- PMID: 27935052
- PMCID: PMC7350397
- DOI: 10.1111/php.12684
An Ethenoadenine FAD Analog Accelerates UV Dimer Repair by DNA Photolyase
Erratum in
-
An Ethenoadenine FAD Analog Accelerates UV Dimer Repair by DNA Photolyase.Photochem Photobiol. 2018 Jan;94(1):195. doi: 10.1111/php.12870. Photochem Photobiol. 2018. PMID: 29342322 No abstract available.
Abstract
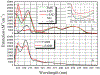
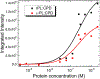
Reduced anionic flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH- ) is the critical cofactor in DNA photolyase (PL) for the repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) in UV-damaged DNA. The initial step involves photoinduced electron transfer from *FADH- to the CPD. The adenine (Ade) moiety is nearly stacked with the flavin ring, an unusual conformation compared to other FAD-dependent proteins. The role of this proximity has not been unequivocally elucidated. Some studies suggest that Ade is a radical intermediate, but others conclude that Ade modulates the electron transfer rate constant (kET ) through superexchange. No study has succeeded in removing or modifying this Ade to test these hypotheses. Here, FAD analogs containing either an ethano- or etheno-bridged Ade between the AN1 and AN6 atoms (e-FAD and ε-FAD, respectively) were used to reconstitute apo-PL, giving e-PL and ε-PL respectively. The reconstitution yield of e-PL was very poor, suggesting that the hydrophobicity of the ethano group prevented its uptake, while ε-PL showed 50% reconstitution yield. The substrate binding constants for ε-PL and rPL were identical. ε-PL showed a 15% higher steady-state repair yield compared to FAD-reconstituted photolyase (rPL). The acceleration of repair in ε-PL is discussed in terms of an ε-Ade radical intermediate vs superexchange mechanism.
© 2016 The American Society of Photobiology.
Figures





References
-
- Taylor J-S (1994) Unraveling the molecular pathway from sunlight to skin cancer. Acc. Chem. Res 27, 76–82.
-
- Minato S and Werbin H (1971) Spectral properties of the chromophoric material associated with the deoxyribonucleic acid photoreactivating enzyme isolated from baker’s yeast. Biochemistry 10, 4503–4508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

