Structural Basis for Inhibitor-Induced Aggregation of HIV Integrase
- PMID: 27935939
- PMCID: PMC5147827
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002584
Structural Basis for Inhibitor-Induced Aggregation of HIV Integrase
Abstract
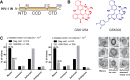
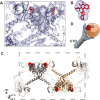
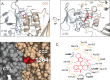
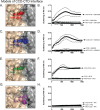
The allosteric inhibitors of integrase (termed ALLINIs) interfere with HIV replication by binding to the viral-encoded integrase (IN) protein. Surprisingly, ALLINIs interfere not with DNA integration but with viral particle assembly late during HIV replication. To investigate the ALLINI inhibitory mechanism, we crystallized full-length HIV-1 IN bound to the ALLINI GSK1264 and determined the structure of the complex at 4.4 Å resolution. The structure shows GSK1264 buried between the IN C-terminal domain (CTD) and the catalytic core domain. In the crystal lattice, the interacting domains are contributed by two different dimers so that IN forms an open polymer mediated by inhibitor-bridged contacts; the N-terminal domains do not participate and are structurally disordered. Engineered amino acid substitutions at the inhibitor interface blocked ALLINI-induced multimerization. HIV escape mutants with reduced sensitivity to ALLINIs commonly altered amino acids at or near the inhibitor-bound interface, and these substitutions also diminished IN multimerization. We propose that ALLINIs inhibit particle assembly by stimulating inappropriate polymerization of IN via interactions between the catalytic core domain and the CTD and that understanding the interface involved offers new routes to inhibitor optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
JJ, EV, PW, and CM are employees of GlaxoSmithKline and may use information contained in this manuscript to improve therapeutics for HIV infection. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimizing the Multimerization Properties of Quinoline-Based Allosteric HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors.Viruses. 2024 Jan 28;16(2):200. doi: 10.3390/v16020200. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38399977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Impact of Ex Vivo Resistance Mutations on HIV-1 Integrase Polymers Induced by Allosteric Inhibitors.J Mol Biol. 2025 Sep 1;437(17):169224. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169224. Epub 2025 May 21. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40409709
-
Allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors promote aberrant protein multimerization by directly mediating inter-subunit interactions: Structural and thermodynamic modeling studies.Protein Sci. 2016 Nov;25(11):1911-1917. doi: 10.1002/pro.2997. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27503276 Free PMC article.
-
The structural and mechanistic bases for the viral resistance to allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitor pirmitegravir.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0046524. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00465-24. Epub 2024 Oct 15. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39404354 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric inhibition of HIV-1 integrase activity.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Jun;17(3):339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.04.010. Epub 2013 May 3. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23647983 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Going beyond Integration: The Emerging Role of HIV-1 Integrase in Virion Morphogenesis.Viruses. 2020 Sep 9;12(9):1005. doi: 10.3390/v12091005. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32916894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of host protein hijacking in human T-cell leukemia virus integration.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 19;11(1):3121. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16963-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32561747 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the amino-terminal sequence on the structure and function of HIV integrase.Retrovirology. 2020 Aug 31;17(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12977-020-00537-x. Retrovirology. 2020. PMID: 32867805 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the Multimerization Properties of Quinoline-Based Allosteric HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors.Viruses. 2024 Jan 28;16(2):200. doi: 10.3390/v16020200. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38399977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological and Structural Analyses of New Potent Allosteric Inhibitors of HIV-1 Integrase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jul 18;67(7):e0046223. doi: 10.1128/aac.00462-23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37310224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christ F, Shaw S, Demeulemeester J, Desimmie BA, Marchand A, Butler S, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of the LEDGF/p75 binding site of integrase block HIV replication and modulate integrase multimerization. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy. 2012;56(8):4365–74. Epub 2012/06/06. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3421592. 10.1128/AAC.00717-12 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng L, Sharma A, Slaughter A, Jena N, Koh Y, Shkriabai N, et al. The A128T resistance mutation reveals aberrant protein multimerization as the primary mechanism of action of allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2013;288(22):15813–20. Epub 2013/04/26. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3668738. 10.1074/jbc.M112.443390 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

