The anti-arthritic activity of total glycosides from Pterocephalus hookeri, a traditional Tibetan herbal medicine
- PMID: 27937009
- PMCID: PMC6130749
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1263869
The anti-arthritic activity of total glycosides from Pterocephalus hookeri, a traditional Tibetan herbal medicine
Abstract
Context: Pterocephalus hookeri (C. B. Clarke) Hock., a traditional Tibetan herbal medicine rich in glycosides, has been used to treat several diseases including rheumatoid arthritis.
Objective: To evaluate the anti-arthritic activity of total glycosides from P. hookeri, and its possible mechanisms of action.
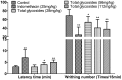
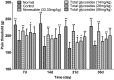
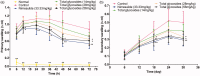
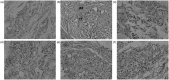
Materials and methods: Anti-arthritic activity of total glycosides from P. hookeri (oral administration for 30 days at 14-56 mg/kg) was evaluated using paw swelling, arthritis scores and histopathological measurement in adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA) Sprague-Dawley rats. The NF-κB p65 expression in synovial tissues, and serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) levels was measured in AA rats, respectively. Further assessment of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of these glycosides were carried out using inflammation and hyperalgesia models induced by xylene, carrageenan, agar and acetic acid, respectively.
Results: Total glycosides (56 mg/kg) decreased the paw swelling (38.0%, p < 0.01), arthritis scores (25.3%, p < 0.01) and synovial inflammation in AA rats. The glycosides significantly (p < 0.05-0.01) attenuated the inflammation induced by xylene, carrageenan, acetic acid and agar, increased the pain threshold in acetic acid-induced writhing in mice and mechanical stimuli-induced hyperalgia in AA rats. The glycosides (14, 28, 56 mg/kg) also suppressed the NF-κB p65 expression (33.1-78.2%, p < 0.05-0.01), reduced MDA (21.3-35.9%, p < 0.01) and NO (20.3-32.4%, p < 0.05-0.01) levels, respectively, enhanced the SOD activity (7.8%, p < 0.05) at 56 mg/kg in AA rats.
Discussion and conclusion: Our findings confirmed the anti-arthritic property of the total glycosides from P. hookeri, which may be attributed to its inhibition on NF-κB signalling and oxidative stress.
Keywords: NF-κB; Pterocephalus hookeri (C. B. Clarke) Hock; Tibetan herbal medicine; adjuvant-induced arthritis; anti-arthritic activity; anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities; oxidative stress; total glycosides.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of a standardizedextract of bis-iridoids from Pterocephalus hookeri.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Apr 24;216:233-238. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.01.035. Epub 2018 Feb 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29410154
-
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of ethanol and aqueous extracts of Pterocephalus hookeri (C.B. Clarke) Höeck.J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jun 25;123(3):510-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.01.039. Epub 2009 Mar 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19443147
-
Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of aqueous extract of Rosa centifolia in experimental rat models.Int J Rheum Dis. 2017 Sep;20(9):1072-1078. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12625. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 26222375
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of Pterocephalus hookeri (C. B. Clarke) Höeck: a review.RSC Adv. 2021 Aug 26;11(46):28761-28774. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05548h. eCollection 2021 Aug 23. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35478563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant polyarthritis in rats: is this a satisfactory model for screening anti-arthritic drugs?Agents Actions. 1982 Oct;12(4):452-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01965926. Agents Actions. 1982. PMID: 6758549 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening and Isolation of Potential Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Saxifraga atrata via Affinity Ultrafiltration-HPLC and Multi-Target Molecular Docking Analyses.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 9;14(12):2405. doi: 10.3390/nu14122405. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745138 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Immunomodulatory Potential of Rosmarinic Acid Isolated from Punica granatum L. using Bioactivity-Guided Approach: In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Approaches.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(36):5969-5988. doi: 10.2174/0109298673291064240227094654. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38445701
-
Structural elucidation and in vivo anti-arthritic activity of β-amyrin and polpunonic acid isolated from the root bark of Ziziphus abyssinica HochstEx. A Rich (Rhamnaceae).Bioorg Chem. 2020 May;98:103744. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103744. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32179280 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicokinetics and Tissue Distribution of the Hepatotoxic Triterpenoid Saponin Pterocephin A in Rats Using the Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) Method.Molecules. 2024 Oct 25;29(21):5044. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215044. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519684 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of sodium deoxycholate tailored deformable-emulsomes of etodolac for effective management of arthritis.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;13(1):21681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46119-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38066008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed AS, Li J, Erlandsson-Harris H, Stark A, Bakalkin G, Ahmed M.. 2012. Suppression of pain and joint destruction by inhibition of the proteasome system in experimental osteoarthritis. Pain. 153:18–26. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf S, Mapp PI, Walsh DA.. 2010. Angiogenesis and the persistence of inflammation in a rat model of proliferative synovitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 62:1890–1898. - PubMed
-
- Asquith DL, Miller AM, McInnes IB, Liew FY.. 2009. Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 39:2040–2044. - PubMed
-
- Bermas BL.2014. Non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids and disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for the management of rheumatoid arthritis before and during pregnancy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 26:334–340. - PubMed
-
- Deraedt R, Jouquey S, Delevallee F, Flahaut M.. 1980. Release of prostaglandins E and F in an algogenic reaction and its inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 11:17–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
