Effects of butanol fraction of Ziziphus mucronata root ethanol extract on glucose homeostasis, serum insulin and other diabetes-related parameters in a murine model for type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 27937039
- PMCID: PMC6130741
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1242632
Effects of butanol fraction of Ziziphus mucronata root ethanol extract on glucose homeostasis, serum insulin and other diabetes-related parameters in a murine model for type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Context: Ziziphus mucronata Willd (Rhamnaceae) is currently used in Nigerian traditional treatment of diabetes mellitus. However, detailed information on the antidiabetic potential of the plant parts is presently unknown.
Objectives: The present study investigated the antidiabetic effects of the butanol fraction of Z. mucronata root (ZMBF) in a type 2 diabetes (T2D) model of rats.
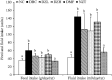
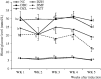
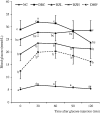
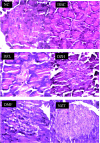
Materials and methods: T2D was induced in rats by feeding a 10% fructose solution ad libitum for two weeks followed by an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (40 mg/kg bw) and the animals were orally treated with ZMBF 150 or 300 mg/kg bw for five days a week for four weeks. Food and fluid intake, body weight changes and blood glucose levels were monitored during the experiment while other blood and organ specific diabetes-associated parameters were measured at the end of the experiment.
Results: After four-week treatment, significantly (p < 0.05) lower blood glucose (19.24 vs 28.96 mmol/L), improved glucose tolerance ability (21.26 vs 28.56 mmol/L), higher serum insulin (131.37 vs 64.20 pmol/L) and liver glycogen (2.40 vs 1.54 mg/g tissue) were observed in the 300 mg/kg ZMBF ingested group compared with the diabetic control group. However, food and fluid intake, body weight gain, HOMA-β, HOMA-IR, serum fructosamine level, hepatic and renal function tests were not significantly (p > 0.05) affected by the treatment of ZMBF.
Conclusion: Results of this study suggest that ZMBF treatment, at 300 mg/kg bw, possess antidiabetic activity, but could not ameliorate some diabetes-related parameters in type 2 diabetic rats.
Keywords: Buffalo thorn; blood glucose; glucose tolerance; insulin resistance; liver glycogen; β-cell function.
Figures

References
-
- Adewusi EA, Steenkamp V.. 2011. In vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activity of medicinal plants from Southern Africa. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 4:829–835. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. 2007. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 30:S42–S47. - PubMed
-
- Boudjelal A, Henchiri C, Siracusa L, Sari M, Ruberto G.. 2012. . Compositional analysis and in vivo anti-diabetic activity of wild Algerian Marrubium vulgare L. infusion. Fitoterapia. 83:286–292. - PubMed
-
- Etuk EU, Bello SO, Isezuo SA, Mohammed BJ.. 2010. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in the north western region of Nigeria. Asian J Exp Biol Sci. 1:55–59.
-
- Farook MS, Atlee WC, Karimulla S, Davey MS.. 2011. Assessment of antidiabetic potential of Caesalpinia digyna Rottler root extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2:675–684.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
