Evaluation of the efficacy of a short-course, personalized self-management and intensive spa therapy intervention as active prevention of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremities (Muska): a research protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27938361
- PMCID: PMC5148841
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1353-8
Evaluation of the efficacy of a short-course, personalized self-management and intensive spa therapy intervention as active prevention of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremities (Muska): a research protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) constitute a major occupational health problem in the working population, substantially impacting the quality of life of employees. They also cause considerable economic cost to the healthcare system, with, notably, the reimbursement of treatments and compensation for lost income. MSDs manifest as localized pain or functional difficulty in one or more anatomical areas, such as the cervical spine, shoulder, elbow, hand, and wrist. Although prevalence varies depending on the region considered and the method of assessment, a prevalence of 30% is found in different epidemiological studies. The disease needs to be prevented, not only for medical and economic reasons, but also for legal reasons, owing to the requirement of assessing occupational risks. The strategy envisaged may thus revolve around active, multimodal prevention that has employees fully involved at the heart of their care. Although physical exercise is widely recommended, few studies with a good level of evidence have enabled us to base a complete, well-constructed intervention on exercise that can be offered as secondary prevention in these disorders.
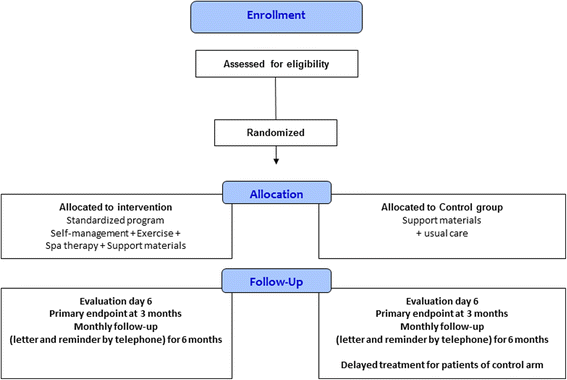
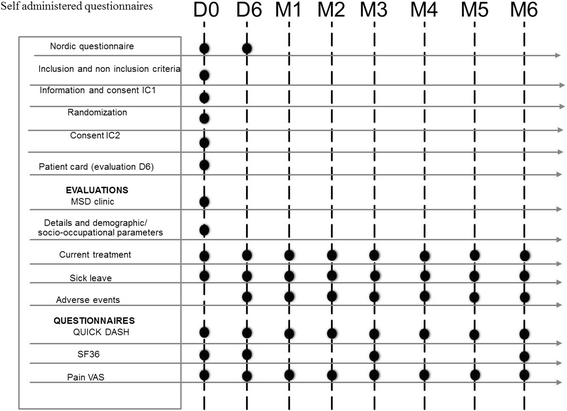
Methods: A prospective, multicenter, comparative (intervention arm vs. control arm), randomized (immediate vs. later treatment) study using Zelen's design. This study falls under active prevention of MSDs of the upper extremities (UE-MSDs). Participants are workers aged between 18 and 65 years with latent or symptomatic MSDS, with any type of job or workstation, with or without an history of sick leave. The primary aim is to show the superiority at 3 months of a combination of spa therapy, exercise, and self-management workshops for 6 days over usual care in the management of MSDs in terms of employee functional capacity in personal and professional daily life. Secondary aims are to assess the benefit of the intervention in terms of pain, quality of life, and accumulated duration of sick leave.
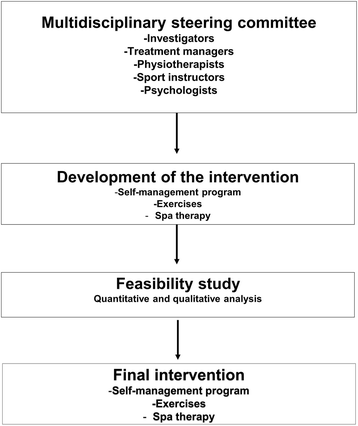
Discussion: This randomized controlled trial is the first that will aim to evaluate multidisciplinary management of UE-MSDs using nonpharmacological treatment combining exercise, self-management, and spa therapy. The originality of this intervention lies, in its short, intensive format, which is compatible with remaining in work; and in its multidisciplinary approach. This trial has the potential to demonstrate, with a good level of evidence, the benefits of a short course of spa therapy combined with a personalized self-management program on the functional capacity, pain, and quality of life of employees in their daily life.
Trial registration: Clinical trial.gov NCT02702466 retrospectively registered.
Protocol: Version 4 of 9/10/2015.
Keywords: Exercise; Musculoskeletal disorders; Prevention; Spa therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[MSDs and job security of employees aged 50 years and over: a challenge for occupational health and public health].Sante Publique. 2008 May-Jun;20 Suppl 3:S19-28. doi: 10.3917/spub.083.0019. Sante Publique. 2008. PMID: 18773826 French.
-
Efficacy of 'Tailored Physical Activity' or 'Chronic Pain Self-Management Program' on return to work for sick-listed citizens: design of a randomised controlled trial.BMC Public Health. 2013 Jan 23;13:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-66. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23343386 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of 40-hour versus 100-hour vocational rehabilitation on work participation for workers on sick leave due to subacute or chronic musculoskeletal pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Jul 28;16:317. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0861-4. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26215748 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prevalence of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Surgeons and Interventionalists: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Surg. 2018 Feb 21;153(2):e174947. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.4947. Epub 2018 Feb 21. JAMA Surg. 2018. PMID: 29282463 Free PMC article.
-
[Work-related musculoskeletal disorders: priority to prevention and coordination of the interventions].Rev Prat. 2014 Mar;64(3):350-7. Rev Prat. 2014. PMID: 24851371 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of self-management exercise program with spa therapy for behavioral management of knee osteoarthritis: research protocol for a quasi-randomized controlled trial (GEET one).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Oct 16;18(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2339-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30326906 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of anaerobic and aerobic exercise on age-related pathways in skeletal muscle.Ageing Res Rev. 2017 Aug;37:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 May 6. Ageing Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28487241 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical