3D culture models of Alzheimer's disease: a road map to a "cure-in-a-dish"
- PMID: 27938410
- PMCID: PMC5148918
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0139-7
3D culture models of Alzheimer's disease: a road map to a "cure-in-a-dish"
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) transgenic mice have been used as a standard AD model for basic mechanistic studies and drug discovery. These mouse models showed symbolic AD pathologies including β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques, gliosis and memory deficits but failed to fully recapitulate AD pathogenic cascades including robust phospho tau (p-tau) accumulation, clear neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and neurodegeneration, solely driven by familial AD (FAD) mutation(s). Recent advances in human stem cell and three-dimensional (3D) culture technologies made it possible to generate novel 3D neural cell culture models that recapitulate AD pathologies including robust Aβ deposition and Aβ-driven NFT-like tau pathology. These new 3D human cell culture models of AD hold a promise for a novel platform that can be used for mechanism studies in human brain-like environment and high-throughput drug screening (HTS). In this review, we will summarize the current progress in recapitulating AD pathogenic cascades in human neural cell culture models using AD patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or genetically modified human stem cell lines. We will also explain how new 3D culture technologies were applied to accelerate Aβ and p-tau pathologies in human neural cell cultures, as compared the standard two-dimensional (2D) culture conditions. Finally, we will discuss a potential impact of the human 3D human neural cell culture models on the AD drug-development process. These revolutionary 3D culture models of AD will contribute to accelerate the discovery of novel AD drugs.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid plaques; High-throughput drug screening; Induced-pluripotent stem cell; Neurofibrillary tangles; Three-dimensional culture.
Figures
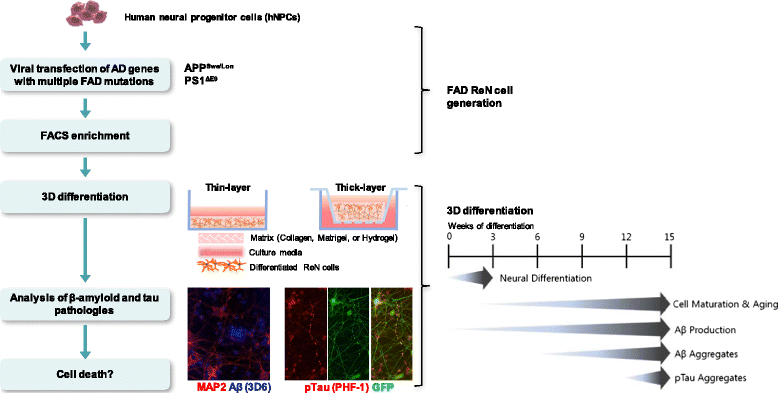
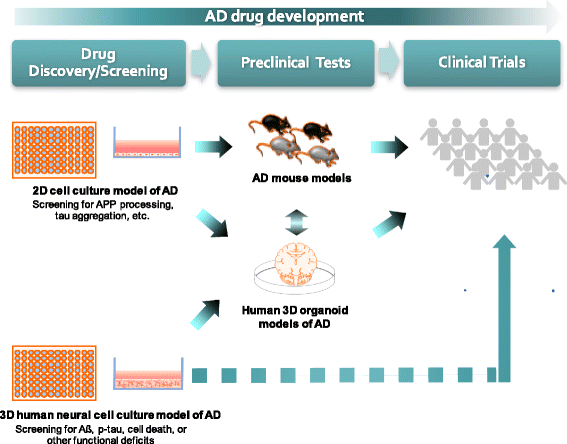
Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's in 3D culture: challenges and perspectives.Bioessays. 2015 Oct;37(10):1139-48. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500063. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26252541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A three-dimensional human neural cell culture model of Alzheimer's disease.Nature. 2014 Nov 13;515(7526):274-8. doi: 10.1038/nature13800. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25307057 Free PMC article.
-
Recapitulating amyloid β and tau pathology in human neural cell culture models: clinical implications.US Neurol. 2015 Fall;11(2):102-105. doi: 10.17925/USN.2015.11.02.102. US Neurol. 2015. PMID: 27019672 Free PMC article.
-
A 3D human neural cell culture system for modeling Alzheimer's disease.Nat Protoc. 2015 Jul;10(7):985-1006. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.065. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Nat Protoc. 2015. PMID: 26068894 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of Alzheimer's disease: the long and filamentous road.Neurol Res. 2003 Sep;25(6):590-600. doi: 10.1179/016164103101202020. Neurol Res. 2003. PMID: 14503012 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Approaches to Studying SLC13A5 Disease.Metabolites. 2024 Jan 24;14(2):84. doi: 10.3390/metabo14020084. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38392976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microphysiological systems for human aging research.Aging Cell. 2024 Mar;23(3):e14070. doi: 10.1111/acel.14070. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38180277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated neuronal aging in vitro ∼melting watch ∼.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;14:868770. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.868770. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36016855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Representing Diversity in the Dish: Using Patient-Derived in Vitro Models to Recreate the Heterogeneity of Neurological Disease.Front Neurosci. 2018 Feb 9;12:56. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00056. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29479303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 3D human iPSC-derived multi-cell type neurosphere system to model cellular responses to chronic amyloidosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Apr 24;22(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03433-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40275379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanzi RE. A brief history of Alzheimer’s disease gene discovery. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(Suppl 1):S5–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

