miR-107 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells by Targeting Prostate Apoptosis Response-4 (Par4)
- PMID: 27938501
- PMCID: PMC7841080
- DOI: 10.3727/096504016X14803476672380
miR-107 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells by Targeting Prostate Apoptosis Response-4 (Par4)
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Oncol Res. 2020 Dec 10;28(5):553-557. doi: 10.3727/096504020X16032056440094. Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 33349308 Free PMC article.
Abstract
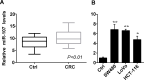
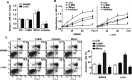
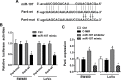
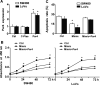
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies in the world, with a high incidence and a high mortality. However, the pathogenesis of CRC carcinogenesis is still unexplored. In this study, we investigated the role of miR-107 in the regulation of CRC cell proliferation and apoptosis. First, the expression of miR-107 was observed to be aberrantly increased in human CRC tumor tissues and cell lines when compared to the colonic control tissues and colon epithelial cells. Further study showed that the proliferative and apoptotic capacities of human CRC SW480 and LoVo cells were aberrantly regulated by miR-107. The proliferation of SW480 and LoVo cells was remarkably enhanced by the miR-107 mimic but suppressed by the miR-107 inhibitor when compared to the negative control. On the contrary, the apoptotic rate of both SW480 and LoVo cells was significantly inhibited by miR-107 overexpression but increased by miR-107 inhibition. In addition, we identified prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par4) as a direct target of miR-107 with a potential binding site on the 3'-UTR of mRNA, as evaluated by bioinformatics prediction and luciferase reporter assay. Par4 expression levels were significantly inhibited by the miR-107 mimic but upregulated by the miR-107 inhibitor in both SW480 and LoVo cells. Compared to the control, the increase in Par4 expression significantly inhibited the induction role of miR-107 in the proliferation of SW480 and LoVo cells, and the apoptotic rate of cells repressed by the miR-107 mimic was also reversed by Par4 overexpression. In summary, our results demonstrated that miR-107 exerts a positive role in the survival of CRC cells by directly targeting Par4. This might reveal a novel understanding about human CRC pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum.Oncol Res. 2020 Dec 10;28(5):553-557. doi: 10.3727/096504020X16032056440094. Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 33349308 Free PMC article.
-
miR-17-3P regulates the proliferation and survival of colon cancer cells by targeting Par4.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):618-623. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7863. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115593
-
miR-132 Regulates Adriamycin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells Through Targeting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019 Aug;34(6):398-404. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2018.2749. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019. Retraction in: Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021 Oct;36(8):705. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2018.2749.retract. PMID: 30939040 Retracted.
-
microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2013 Oct 17;32(42):5078-88. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.526. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23208495
-
The rs7911488-T allele promotes the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer through modulating miR-1307/PRRX1.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 7;11(8):651. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02834-x. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32811812 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Screening key miRNAs and genes in prostate cancer by microarray analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):856-868. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.30. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117431 Free PMC article.
-
miR-107 regulates growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells via activation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway by down-regulating FAT4.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(11):5264-5273. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2396. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31297980 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA TMPO-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through sponging miR-329-3p to stimulate FOXK1-mediated AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2020 Jul;9(14):5235-5246. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3046. Epub 2020 May 27. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32462698 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumour Cell Associated MicroRNA Profiles Change during Chemoradiation and Are Predictive of Response in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 20;15(16):4184. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164184. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627212 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) triggers cell apoptosis via ROS-caused mitochondrial dysfunction in colorectal carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug;149(10):6883-6899. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04624-2. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36810816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen H, Dean DB, Zhang C. MicroRNA expression signature and antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of MicroRNA in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Cir Res. 2007;100:1579–88. - PubMed
-
- Haigis KM. Molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;11:609–33.
-
- Fearon ER. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Ann Rev Pathol. 2011;6:479–507. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
