MicroRNA-181b Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Invasion of Glioma Cells via Targeting Sal-Like Protein 4
- PMID: 27938503
- PMCID: PMC7841051
- DOI: 10.3727/096504016X14791732531006
MicroRNA-181b Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Invasion of Glioma Cells via Targeting Sal-Like Protein 4
Abstract
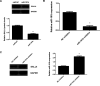
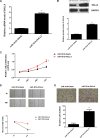
MicroRNAs (miRs), a class of noncoding RNAs that are 18-25 nucleotides in length, are able to suppress gene expression by targeting complementary regions of mRNAs and inhibiting protein translation. Recently, miR-181b was found to play a suppressive role in glioma, but the regulatory mechanism of miR-181b in the malignant phenotypes of glioma cells remains largely unclear. In this study, we found that miR-181b was significantly downregulated in glioma tissues when compared with normal brain tissues, and decreased miR-181b levels were significantly associated with high-grade pathology and a poor prognosis for patients with glioma. Moreover, miR-181b was downregulated in glioma cell lines (U87, SHG44, U373, and U251) compared to normal astrocytes. Overexpression of miR-181b significantly decreased the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma U251 cells. Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4) was identified as a novel target gene of miR-181b in U251 cells. The expression of SALL4 was significantly upregulated in glioma tissues and cell lines, and an inverse correlation was observed between the miR-181b and SALL4 expression levels in glioma. Further investigation showed that the protein expression of SALL4 was negatively regulated by miR-181b in U251 cells. Knockdown of SALL4 significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of U251 cells, while overexpression of SALL4 effectively reversed the suppressive effects of miR-181b on these malignant phenotypes of U251 cells. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that miR-181b has a suppressive effect on the malignant phenotypes of glioma cells, at least partly, by directly targeting SALL4. Therefore, the miR-181b/SALL4 axis may become a potential therapeutic target for glioma.
Figures




References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Yan Y, Jiang Y. RACK1 affects glioma cell growth and differentiation through the CNTN2-mediated RTK/Ras/MAPK pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37:251–7. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004;431:350–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
