The Effect of Skin Pigmentation on the Accuracy of Pulse Oximetry in Infants with Hypoxemia
- PMID: 27939107
- PMCID: PMC5328979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.11.043
The Effect of Skin Pigmentation on the Accuracy of Pulse Oximetry in Infants with Hypoxemia
Abstract
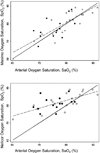
To compare pulse oximetry measurement bias between infants with hypoxemia with either dark skin or light skin with Masimo Radical 7 and Nellcor Oximax. There was no significant difference in systematic bias based on skin pigment for either oximeter.
Keywords: accuracy; infant; oxygen saturation; pulse oximetry.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fouzas S, Priftis KN, Anthracopoulos MB. Pulse oximetry in pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2011;128:740–752. - PubMed
-
- Feiner JR, Severinghaus JW, Bickler PE. Dark skin decreases the accuracy of pulse oximeters at low oxygen saturation: the effects of oximeter probe type and gender. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:S18–S23. - PubMed
-
- Bickler PE, Feiner JR, Severinghaus JW. Effects of skin pigmentation on pulse oximeter accuracy at low saturation. Anesthesiology. 2005;102:715–719. - PubMed
-
- Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Inc. Rapidlab 1200 systems operator’s guide. Malvern (PA): Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Inc; 2012. 02087462 Rev. W.
-
- Ries AL, Prewitt LM, Johnson JJ. Skin color and ear oximetry. Chest. 1989;96:287–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

