Changes in adipose tissue cellular composition during obesity and aging as a cause of metabolic dysregulation
- PMID: 27939445
- PMCID: PMC5466486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.12.007
Changes in adipose tissue cellular composition during obesity and aging as a cause of metabolic dysregulation
Abstract
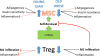
Adipose tissue represents complex endocrine organ containing several different cellular populations including adipocytes, pre-adipocytes, mesenchymal stem cells, macrophages and lymphocytes. It is well establishing that these populations are not static but alter during obesity and aging. Changes in cellular populations alter inflammatory status and other common metabolic complications arise, therefore adipose tissue cellular composition helps dictate its endocrine and regulatory function. During excessive weight gain in obese individuals and as we age there is shift towards increase populations of inflammatory macrophages with a decrease of regulatory T cell. This altered cellular composition promote chronic low grade inflammation negatively affecting mesenchymal stem cell progenitor self-renewal, which result in deterioration of adipogenesis and increased cellular stress in adipocytes. All these changes promote metabolic disorders including age- or obese-related insulin resistance leading to type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bartke A, Brown-Borg H. Life extension in the dwarf mouse. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2004;63:189–225. - PubMed
-
- Barzilai N, She L, Liu BQ, Vuguin P, Cohen P, Wang J, Rossetti L. Surgical removal of visceral fat reverses hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1999;48:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Cancello R, Tordjman J, Poitou C, Guilhem G, Bouillot JL, Hugol D, Coussieu C, Basdevant A, Hen AB, Bedossa P, et al. Increased Infiltration of Macrophages in Omental Adipose Tissue Is Associated With Marked Hepatic Lesions in Morbid Human Obesity. Diabetes. 2006;55:1554–1561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

