Cloning and functional characterizations of an apoptogenic Hid gene in the Scuttle Fly, Megaselia scalaris (Diptera; Phoridae)
- PMID: 27940109
- PMCID: PMC5295500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.11.043
Cloning and functional characterizations of an apoptogenic Hid gene in the Scuttle Fly, Megaselia scalaris (Diptera; Phoridae)
Abstract
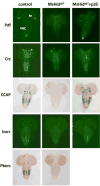
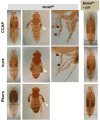
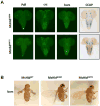
Although the mechanisms of apoptotic cell death have been well studied in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, it is unclear whether such mechanisms are conserved in other distantly related species. Using degenerate primers and PCR, we cloned a proapoptotic gene homologous to Head involution defective (Hid) from the Scuttle fly, Megaselia scalaris (MsHid). MsHid cDNA encodes a 197-amino acid-long polypeptide, which so far is the smallest HID protein. PCR analyses revealed that the MsHid gene consists of four exons and three introns. Ectopic expression of MsHid in various peptidergic neurons and non-neuronal tissues in Drosophila effectively induced apoptosis of these cells. However, deletion of either conserved domain, N-terminal IBM or C-terminal MTS, abolished the apoptogenic activity of MsHID, indicating that these two domains are indispensable. Expression of MsHid was found in all life stages, but more prominently in embryos and pupae. MsHid is actively expressed in the central nervous system (CNS), indicating its important role in CNS development. Together MsHID is likely to be an important cell death inducer during embryonic and post-embryonic development in this species. In addition, we found 2-fold induction of MsHid expression in UV-irradiated embryos, indicating a possible role for MsHid in UV-induced apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Evolution; Hid; Peptidergic neurons.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall KA, Steller H. Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell. 1998;95:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Tugentman M, Shilo BZ, Steller H. Regulation of cell number by MAPK-dependent control of apoptosis: a mechanism for trophic survival signaling. Dev Cell. 2002;2:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 2003;113:25–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

