A Target-Less Vision-Based Displacement Sensor Based on Image Convex Hull Optimization for Measuring the Dynamic Response of Building Structures
- PMID: 27941635
- PMCID: PMC5191066
- DOI: 10.3390/s16122085
A Target-Less Vision-Based Displacement Sensor Based on Image Convex Hull Optimization for Measuring the Dynamic Response of Building Structures
Abstract
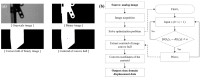
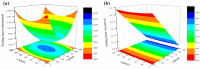
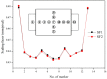
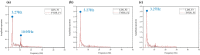
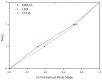
Existing vision-based displacement sensors (VDSs) extract displacement data through changes in the movement of a target that is identified within the image using natural or artificial structure markers. A target-less vision-based displacement sensor (hereafter called "TVDS") is proposed. It can extract displacement data without targets, which then serve as feature points in the image of the structure. The TVDS can extract and track the feature points without the target in the image through image convex hull optimization, which is done to adjust the threshold values and to optimize them so that they can have the same convex hull in every image frame and so that the center of the convex hull is the feature point. In addition, the pixel coordinates of the feature point can be converted to physical coordinates through a scaling factor map calculated based on the distance, angle, and focal length between the camera and target. The accuracy of the proposed scaling factor map was verified through an experiment in which the diameter of a circular marker was estimated. A white-noise excitation test was conducted, and the reliability of the displacement data obtained from the TVDS was analyzed by comparing the displacement data of the structure measured with a laser displacement sensor (LDS). The dynamic characteristics of the structure, such as the mode shape and natural frequency, were extracted using the obtained displacement data, and were compared with the numerical analysis results. TVDS yielded highly reliable displacement data and highly accurate dynamic characteristics, such as the natural frequency and mode shape of the structure. As the proposed TVDS can easily extract the displacement data even without artificial or natural markers, it has the advantage of extracting displacement data from any portion of the structure in the image.
Keywords: dynamic characteristics; image convex hull; non-marker; scaling factor map; vision-based displacement sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of Marker-Free Night-Vision Displacement Sensor System by Using Image Convex Hull Optimization.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 27;18(12):4151. doi: 10.3390/s18124151. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30486349 Free PMC article.
-
A Vision-Based Sensor for Noncontact Structural Displacement Measurement.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jul 9;15(7):16557-75. doi: 10.3390/s150716557. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26184197 Free PMC article.
-
Building Coarse to Fine Convex Hulls With Auxiliary Vertices for Palette-Based Image Recoloring.IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2024 Aug;30(8):5581-5595. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2023.3296386. Epub 2024 Jul 1. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2024. PMID: 37463085
-
Non-Target Structural Displacement Measurement Using Reference Frame-Based Deepflow.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jul 7;19(13):2992. doi: 10.3390/s19132992. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31284647 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability Assessment of a Vision-Based Dynamic Displacement Measurement System Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;23(6):3232. doi: 10.3390/s23063232. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36991942 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cross-Correlation-Based Structural System Identification Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Sep 11;17(9):2075. doi: 10.3390/s17092075. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28891985 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a High Precision Displacement Measurement System by Fusing a Low Cost RTK-GPS Sensor and a Force Feedback Accelerometer for Infrastructure Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Nov 28;17(12):2745. doi: 10.3390/s17122745. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29182563 Free PMC article.
-
Vision-Based Building Seismic Displacement Measurement by Stratification of Projective Rectification Using Lines.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 12;20(20):5775. doi: 10.3390/s20205775. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33053806 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Marker-Free Night-Vision Displacement Sensor System by Using Image Convex Hull Optimization.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 27;18(12):4151. doi: 10.3390/s18124151. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30486349 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Contact Measurement of the Surface Displacement of a Slope Based on a Smart Binocular Vision System.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 31;18(9):2890. doi: 10.3390/s18092890. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30200371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choi I., Kim J.H., You Y.-C. Effect of cyclic loading on composite behavior of insulated concrete sandwich wall panels with GFRP shear connectors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016;96:7–19. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.04.030. - DOI
-
- Xu Z., Lu X., Guan H., Han B., Ren A. Seismic damage simulation in urban areas based on a high-fidelity structural model and a physics engine. Nat. Hazards. 2014;71:1679–1693. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0972-8. - DOI
-
- Haber R., Unbehauen H. Structure identification of nonlinear dynamic systems—A survey on input/output approaches. Automatica. 1990;26:651–677. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(90)90044-I. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

