Roles of Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 (Erdr1) on Inflammatory Skin Diseases
- PMID: 27941650
- PMCID: PMC5187859
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17122059
Roles of Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 (Erdr1) on Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Abstract
Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 (Erdr1) is known as a hemoglobin synthesis factor which also regulates cell survival under conditions of stress. In addition, previous studies have revealed the effects of Erdr1 on cancer progression and its negative correlation with interleukin (IL)-18, a pro-inflammatory cytokine. Based on this evidence, the therapeutic effects of Erdr1 have been demonstrated in several inflammatory skin diseases such as malignant skin cancer, psoriasis, and rosacea. This article reviews the roles of Erdr1 in skin inflammation, suggesting that Erdr1 is a potential therapeutic molecule on inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: Erdr1; IL-18; cutaneous inflammation; melanoma; psoriasis; rosacea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unveiling the role of lncRNA ERDR1 in immune cell regulation.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 17;11(3):e42085. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42085. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39991241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
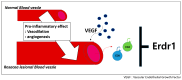
Recombinant erythroid differentiation regulator 1 inhibits both inflammation and angiogenesis in a mouse model of rosacea.Exp Dermatol. 2015 Sep;24(9):680-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12745. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25940661
-
Therapeutic Effects of Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 on Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 17;17(2):244. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020244. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26901187 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 as a Novel Biomarker for Hair Loss Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 3;18(2):316. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020316. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28165377 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 (ERDR1) in the Control of Proliferation and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 9;21(7):2603. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072603. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32283647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 as a Regulator of Neuronal GSH Synthesis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;13(7):771. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070771. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061840 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the role of lncRNA ERDR1 in immune cell regulation.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 17;11(3):e42085. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42085. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39991241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosacea, microbiome and probiotics: the gut-skin axis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1323644. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1323644. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38260914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of IL18 in Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17170. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417170. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Treatment Approaches for Cutaneous Field Cancerization.Curr Dermatol Rep. 2019 Sep;8(3):122-132. doi: 10.1007/s13671-019-00265-2. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31475077 Free PMC article.
References
-
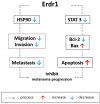
- Jung M.K., Park Y., Song S.B., Cheon S.Y., Park S., Houh Y., Ha S., Kim H.J., Park J.M., Kim T.S., et al. Erythroid differentiation regulator 1, an interleukin 18-regulated gene, acts as a metastasis suppressor in melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011;131:2096–2104. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.170. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jung M.K., Houh Y.K., Ha S., Yang Y., Kim D., Kim T.S., Yoon S.R., Bang S.I., Cho B.J., Lee W.J., et al. Recombinant Erdr1 suppresses the migration and invasion ability of human gastric cancer cells, SNU-216, through the JNK pathway. Immunol. Lett. 2013;150:145–151. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

