CD4/CD8 Ratio and KT Ratio Predict Yellow Fever Vaccine Immunogenicity in HIV-Infected Patients
- PMID: 27941965
- PMCID: PMC5179051
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005219
CD4/CD8 Ratio and KT Ratio Predict Yellow Fever Vaccine Immunogenicity in HIV-Infected Patients
Abstract
Background: HIV-infected individuals have deficient responses to Yellow Fever vaccine (YFV) and may be at higher risk for adverse events (AE). Chronic immune activation-characterized by low CD4/CD8 ratio or high indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 (IDO) activity-may influence vaccine response in this population.
Methods: We prospectively assessed AE, viremia by the YFV virus and YF-specific neutralizing antibodies (NAb) in HIV-infected (CD4>350) and -uninfected adults through 1 year after vaccination. The effect of HIV status on initial antibody response to YFV was measured during the first 3 months following vaccination, while the effect on persistence of antibody response was measured one year following vaccination. We explored CD4/CD8 ratio, IDO activity (plasma kynurenine/tryptophan [KT] ratio) and viremia by Human Pegivirus as potential predictors of NAb response to YFV among HIV-infected participants with linear mixed models.
Results: 12 HIV-infected and 45-uninfected participants were included in the final analysis. HIV was not significantly associated with AE, YFV viremia or NAb titers through the first 3 months following vaccination. However, HIV-infected participants had 0.32 times the NAb titers observed for HIV-uninfected participants at 1 year following YFV (95% CI 0.13 to 0.83, p = 0.021), independent of sex, age and prior vaccination. In HIV-infected participants, each 10% increase in CD4/CD8 ratio predicted a mean 21% higher post-baseline YFV Nab titer (p = 0.024). Similarly, each 10% increase in KT ratio predicted a mean 21% lower post-baseline YFV Nab titer (p = 0.009). Viremia by Human Pegivirus was not significantly associated with NAb titers.
Conclusions: HIV infection appears to decrease the durability of NAb responses to YFV, an effect that may be predicted by lower CD4/CD8 ratio or higher KT ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
MSF, MS and SBL are employees at Bio-manguinhos-FIOCRUZ, the main national manufacturer of yellow fever vaccine in Brazil. All remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
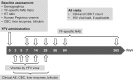
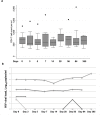
References
-
- Schouten J, Wit FW, Stolte IG, Kootstra NA, van der Valk M, Geerlings SE, et al. Cross-sectional Comparison of the Prevalence of Age-Associated Comorbidities and Their Risk Factors Between HIV-Infected and Uninfected Individuals: The AGEhIV Cohort Study. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2014. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg A, Gona P, Nachman SA, Defechereux P, Yogev R, Hughes W, et al. Antibody responses to hepatitis A virus vaccine in HIV-infected children with evidence of immunologic reconstitution while receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2006;193(2):302–11. 10.1086/498979 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

