Biophysical Studies of the Induced Dimerization of Human VEGF Receptor 1 Binding Domain by Divalent Metals Competing with VEGF-A
- PMID: 27942001
- PMCID: PMC5152890
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167755
Biophysical Studies of the Induced Dimerization of Human VEGF Receptor 1 Binding Domain by Divalent Metals Competing with VEGF-A
Abstract
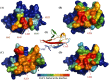
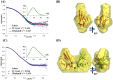
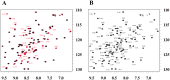
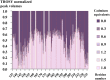
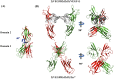
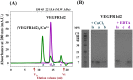
Angiogenesis is tightly regulated through the binding of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) to their receptors (VEGFRs). In this context, we showed that human VEGFR1 domain 2 crystallizes in the presence of Zn2+, Co2+ or Cu2+ as a dimer that forms via metal-ion interactions and interlocked hydrophobic surfaces. SAXS, NMR and size exclusion chromatography analyses confirm the formation of this dimer in solution in the presence of Co2+, Cd2+ or Cu2+. Since the metal-induced dimerization masks the VEGFs binding surface, we investigated the ability of metal ions to displace the VEGF-A binding to hVEGFR1: using a competition assay, we evidenced that the metals displaced the VEGF-A binding to hVEGFR1 extracellular domain binding at micromolar level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- DiSalvo J, Bayne ML, Conn G, Kwok PW, Trivedi PG, Soderman DD, et al. Purification and characterization of a naturally occurring vascular endothelial growth factor.placenta growth factor heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(13):7717–23. Epub 1995/03/31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

