The DPP4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Protects from Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 27942008
- PMCID: PMC5152931
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167853
The DPP4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Protects from Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
Background/aims: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes, however, their influence on the retinal neurovascular unit remains unclear.
Methods: Vasculo- and neuroprotective effects were assessed in experimental diabetic retinopathy and high glucose-cultivated C. elegans, respectively. In STZ-diabetic Wistar rats (diabetes duration of 24 weeks), DPP4 activity (fluorometric assay), GLP-1 (ELISA), methylglyoxal (LC-MS/MS), acellular capillaries and pericytes (quantitative retinal morphometry), SDF-1a and heme oxygenase-1 (ELISA), HMGB-1, Iba1 and Thy1.1 (immunohistochemistry), nuclei in the ganglion cell layer, GFAP (western blot), and IL-1beta, Icam1, Cxcr4, catalase and beta-actin (quantitative RT-PCR) were determined. In C. elegans, neuronal function was determined using worm tracking software.
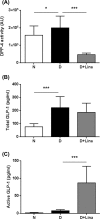
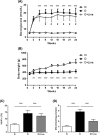
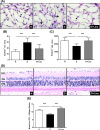
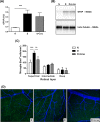
Results: Linagliptin decreased DPP4 activity by 77% and resulted in an 11.5-fold increase in active GLP-1. Blood glucose and HbA1c were reduced by 13% and 14% and retinal methylglyoxal by 66%. The increase in acellular capillaries was diminished by 70% and linagliptin prevented the loss of pericytes and retinal ganglion cells. The rise in Iba-1 positive microglia was reduced by 73% with linagliptin. In addition, the increase in retinal Il1b expression was decreased by 65%. As a functional correlate, impairment of motility (body bending frequency) was significantly prevented in C. elegans.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that linagliptin has a protective effect on the microvasculature of the diabetic retina, most likely due to a combination of neuroprotective and antioxidative effects of linagliptin on the neurovascular unit.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. S.B. is recipient of a stipend from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (International Research Training group 880 Vascular Medicine). T.K. is employed by Boehringer-Ingelheim. H.P.H. has received speaker’s honorarium and a travel grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. Our commercial affiliation involved provision of linagliptin, measurement of DPP-4 activity and GLP-1 levels by Boehringer Ingelheim. We believe that provision of these services did not influence the integrity of our work or alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-angiogenic effects of the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin via inhibition of VEGFR signalling in the mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy.Diabetologia. 2018 Nov;61(11):2412-2421. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4701-4. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30097694
-
The effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide on experimental diabetic retinopathy.Acta Diabetol. 2023 Nov;60(11):1551-1565. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02135-7. Epub 2023 Jul 9. Acta Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37423944 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 is upregulated by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and has protective roles in progressive diabetic nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2016 Oct;90(4):783-96. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27475229
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of linagliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, with consideration of Asian patient populations.J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Jan;8(1):19-28. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12528. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 27180612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linagliptin: a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor with a unique place in therapy.Adv Ther. 2011 Jun;28(6):447-59. doi: 10.1007/s12325-011-0028-y. Epub 2011 May 17. Adv Ther. 2011. PMID: 21603986 Review.
Cited by
-
Cathepsin D plays a role in endothelial-pericyte interactions during alteration of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy.FASEB J. 2018 May;32(5):2539-2548. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700781RR. Epub 2017 Dec 20. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29263022 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1R Activation in the Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 17;23(20):12428. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012428. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimum Effective Dose of DPP-4 Inhibitors for Treating Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy in an Experimental Model.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 16;10(2):465. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020465. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203674 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Stimulation Inhibits Laser-Induced Choroidal Neovascularization by Suppressing Intraocular Inflammation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 May 1;66(5):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332908 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of diabetes on microglial physiology: a systematic review of in vitro, preclinical and clinical studies.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Mar 3;20(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02740-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36869375 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

