Hydroxycholesterol Levels in the Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Revealed by LC-Ag+CIS/MS/MS and LC-ESI/MS/MS with Picolinic Derivatization: Increased Levels and Association with Disability during Acute Attack
- PMID: 27942009
- PMCID: PMC5152860
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167819
Hydroxycholesterol Levels in the Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Revealed by LC-Ag+CIS/MS/MS and LC-ESI/MS/MS with Picolinic Derivatization: Increased Levels and Association with Disability during Acute Attack
Abstract
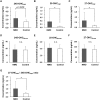
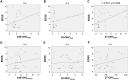
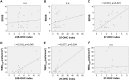
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). Hydroxycholesterols (OHCs), metabolites of CNS cholesterol, are involved in diverse cellular responses to inflammation and demyelination, and may also be involved in the pathogenesis of NMO. We aimed to develop a sensitive and reliable method for the quantitative analysis of three major OHCs (24S-, 25-, and 27-OHCs), and to evaluate their concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum of patients with NMO. The levels of the three OHCs in the serum and CSF were measured using liquid chromatography-silver ion coordination ionspray tandem mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry with picolinyl ester derivatization, respectively. The linear range was 5-250 ng/mL for 24S- and 27-OHC, and 0.5-25 ng/mL for 25-OHC in serum, and was 0.1-5 ng/mL for 24S- and 27-OHC, and 0.03-1 ng/mL for 25-OHC in CSF. Precision and accuracy were 0.5%-14.7% and 92.5%-109.7%, respectively, in serum, and were 0.8%-7.7% and 94.5%-119.2%, respectively, in CSF. Extraction recovery was 82.7%-90.7% in serum and 68.4%-105.0% in CSF. When analyzed in 26 NMO patients and 23 control patients, the 25-OHC (0.54 ± 0.96 ng/mL vs. 0.09 ± 0.04 ng/mL, p = 0.032) and 27-OHC (2.68 ± 3.18 ng/mL vs. 0.68 ± 0.25 ng/mL, p = 0.005) were increased in the CSF from NMO patients. When we measured the OHCCSF index that controls the effects of blood-brain barrier disruption on the level of OHC in the CSF, the 27-OHCCSF index was associated with disability (0.723; 95% confidence interval (CI)- 0.181, 0.620; p = 0.002), while the 24-OHCCSF index (0.518; 95% CI- 1.070, 38.121; p = 0.040) and 25-OHCCSF index (0.677; 95% CI- 4.313, 18.532; p = 0.004) were associated with the number of white blood cells in the CSF of NMO patients. Our results imply that OHCs in the CNS could play a role in the pathogenesis of NMO.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum and CSF N-acetyl aspartate levels differ in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011 Dec;82(12):1355-9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2011.241836. Epub 2011 May 27. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21622936
-
Urinary trypsin inhibitor levels are reduced in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica patients during relapse.Neurochem Int. 2015 Feb;81:28-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Neurochem Int. 2015. PMID: 25555815
-
Blood-brain barrier disruption is more severe in neuromyelitis optica than in multiple sclerosis and correlates with clinical disability.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(4):1483-91. doi: 10.1177/147323001204000427. J Int Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22971500
-
Overlapping CNS inflammatory diseases: differentiating features of NMO and MS.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015 Jan;86(1):20-5. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-308984. Epub 2014 Sep 23. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25248365 Review.
-
On the fluxes of side-chain oxidized oxysterols across blood-brain and blood-CSF barriers and origin of these steroids in CSF (Review).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Apr;188:86-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.12.009. Epub 2018 Dec 23. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30586624 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive review of neuromyelitis optica and clinical characteristics of neuromyelitis optica patients in Puerto Rico.Surg Neurol Int. 2018 Dec 3;9:242. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_224_18. eCollection 2018. Surg Neurol Int. 2018. PMID: 30603227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol is involved in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):11855-11867. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14416. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28060747 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Profiling in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Biomarker Discovery.Metabolites. 2020 Sep 18;10(9):374. doi: 10.3390/metabo10090374. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32961928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxysterol 25-hydroxycholesterol as a metabolic pathophysiological factors of osteoarthritis induces apoptosis in primary rat chondrocytes.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 May 1;24(3):249-257. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.3.249. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32392916 Free PMC article.
-
The technical reliability and biotemporal stability of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for profiling multiple pathophysiologies in Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 5;13(3):e0193707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193707. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29505610 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

