Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 27942595
- PMCID: PMC5135277
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.90558
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
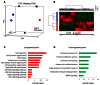
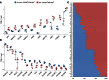
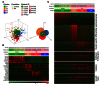
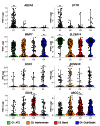
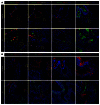
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a lethal interstitial lung disease characterized by airway remodeling, inflammation, alveolar destruction, and fibrosis. We utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to identify epithelial cell types and associated biological processes involved in the pathogenesis of IPF. Transcriptomic analysis of normal human lung epithelial cells defined gene expression patterns associated with highly differentiated alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells, indicated by enrichment of RNAs critical for surfactant homeostasis. In contrast, scRNA-seq of IPF cells identified 3 distinct subsets of epithelial cell types with characteristics of conducting airway basal and goblet cells and an additional atypical transitional cell that contributes to pathological processes in IPF. Individual IPF cells frequently coexpressed alveolar type 1 (AT1), AT2, and conducting airway selective markers, demonstrating "indeterminate" states of differentiation not seen in normal lung development. Pathway analysis predicted aberrant activation of canonical signaling via TGF-β, HIPPO/YAP, P53, WNT, and AKT/PI3K. Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy identified the disruption of alveolar structure and loss of the normal proximal-peripheral differentiation of pulmonary epithelial cells. scRNA-seq analyses identified loss of normal epithelial cell identities and unique contributions of epithelial cells to the pathogenesis of IPF. The present study provides a rich data source to further explore lung health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL136722/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL123969/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007752/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL110964/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL110967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108793/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070549/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131661/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

