The Efficacy of IDegLira (Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide Combination) in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist and Oral Therapy: DUAL III Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 27943107
- PMCID: PMC5306117
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-016-0218-3
The Efficacy of IDegLira (Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide Combination) in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist and Oral Therapy: DUAL III Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: The progressive nature of type 2 diabetes necessitates treatment intensification. This often involves intensification with oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs) initially, followed by other agents, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), with the majority of patients eventually requiring insulin therapy. Therefore, this trial aimed to investigate the efficacy of IDegLira (combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide) in controlling glycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately controlled on a GLP-1RA and OADs.
Methods: In this 26-week open-label phase 3b trial, patients on maximum-dose GLP-1RA therapy (liraglutide once daily or exenatide twice daily) with metformin alone or with pioglitazone and/or sulfonylurea were randomized 2:1 to IDegLira once daily (n = 292) or to unchanged GLP-1RA therapy (n = 146), continuing OADs at the pre-trial dose.
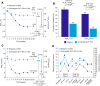
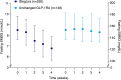
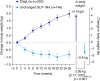
Results: After 26 weeks, HbA1c reductions were superior with IDegLira versus unchanged GLP-1RA; estimated treatment difference -0.94% (-10.3 mmol/mol), p < 0.001. Mean HbA1c reduced from 7.8% to 6.4% (61.5 to 46.9 mmol/mol) with IDegLira and from 7.7 to 7.4% (60.8 to 57.1 mmol/mol) with unchanged GLP-1RA. With IDegLira, 75% and 63% of patients achieved HbA1c <7% and ≤6.5%, compared with 36% and 23% on unchanged GLP-1RA, respectively. Fasting plasma glucose and 9-point self-monitored blood glucose profiles improved significantly more with IDegLira versus unchanged GLP-1RA. The mean change in weight was +2.0 kg with IDegLira, versus -0.8 kg with unchanged GLP-1RA. Rates of confirmed hypoglycemia were low, but higher with IDegLira versus unchanged GLP-1RA. The safety profile of IDegLira was consistent with previous findings; both treatments were well tolerated and the rate of nausea was low in both groups. IDegLira improved patient-reported outcomes versus unchanged GLP-1RA.
Conclusions: IDegLira provided superior glycemic control versus unchanged GLP-1RA and represents an efficacious intensification approach in patients inadequately controlled on GLP-1RAs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov #NCT01676116.
Funding: Novo Nordisk.
Keywords: Clinical trial; GLP-1 receptor agonist; IDegLira; Insulin therapy; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140–149. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2441. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:193–203. doi: 10.2337/dc08-9025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

