Immediate improvement in the cranio-cervical flexion test associated with MDT-based interventions: a case report
- PMID: 27956822
- PMCID: PMC5125429
- DOI: 10.1179/2042618614Y.0000000081
Immediate improvement in the cranio-cervical flexion test associated with MDT-based interventions: a case report
Abstract
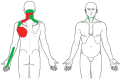
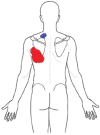
The patient in this case study presented with constant idiopathic neck pain and left lower scapular pain (greater than 3 months) and was treated based on the principles of Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy (MDT). Retraction exercises produced centralization of the lower scapular pain to the upper part of the scapula at the initial visit. At the first visit, the performance level on the Cranio-Cervical Flexion Test (CCFT) was ≤20 mmHg before the treatment. At the conclusion of the treatment during which centralization occurred, the CCFT level improved to 24 mmHg. At the second visit, all symptoms were abolished and cervical range of motion (ROM) was fully restored by performing repeated extension in lying from a retracted position with clinician's traction. The CCFT levels before and immediately after the treatment were 24 and 26 mmHg, respectively. At the third visit (1 week after the initial visit), he noted that all daily activities could be performed without pain. The CCFT level was maintained at 26mmHg. The patient in this study showed immediate improvement in the CCFT through the treatments based on MDT. This suggests a possible link between MDT interventions and motor control of the cervical spine and a need to further investigate this relationship.
Keywords: Assessment; Deep cervical flexors; MDT; McKenzie; Motor control; Neck pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immediate effects of active cranio-cervical flexion exercise versus passive mobilisation of the upper cervical spine on pain and performance on the cranio-cervical flexion test.Man Ther. 2014 Feb;19(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Man Ther. 2014. PMID: 23806488 Clinical Trial.
-
Can a functional postural exercise improve performance in the cranio-cervical flexion test?--a preliminary study.Man Ther. 2012 Jun;17(3):219-24. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2011.12.005. Epub 2012 Feb 4. Man Ther. 2012. PMID: 22310655 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship between cranio-cervical flexion range of motion and pressure change during the cranio-cervical flexion test.Man Ther. 2003 May;8(2):92-6. doi: 10.1016/s1356-689x(03)00008-0. Man Ther. 2003. PMID: 12890436
-
Clinical assessment of the deep cervical flexor muscles: the craniocervical flexion test.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2008 Sep;31(7):525-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.08.003. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18804003 Review.
-
A specific exercise program and modification of postural alignment for treatment of cervicogenic headache: a case report.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2005 Jan;35(1):3-15. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2005.35.1.3. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2005. PMID: 15754599 Review.
Cited by
-
KOJI AWARENESS, a self-rating whole-body movement assessment system, has intersession reliability and comparability to external examiner rating.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 15;19(8):e0308973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308973. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39146306 Free PMC article.
-
McKenzie neck exercise versus cranio-cervical flexion exercise on strength and endurance of deep neck flexor muscles, pain, disability, and craniovertebral angle in individuals with chronic neck pain: a randomized clinical trial.J Man Manip Ther. 2024 Dec;32(6):573-583. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2024.2337979. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Man Manip Ther. 2024. PMID: 38570915 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanical diagnosis and therapy enhances attitude toward self-management in people with musculoskeletal disorders: A preliminary evidence with a before-after design.SAGE Open Med. 2017 Nov 8;5:2050312117740986. doi: 10.1177/2050312117740986. eCollection 2017. SAGE Open Med. 2017. PMID: 29163947 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate neck hypoalgesic effects of craniocervical flexion exercises and cervical retraction exercises among individuals with non-acute neck pain and a directional preference for retraction or extension: preliminary pretest-posttest randomized experimental design.J Man Manip Ther. 2023 Oct;31(5):368-375. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2023.2201918. Epub 2023 Apr 13. J Man Manip Ther. 2023. PMID: 37052492 Free PMC article.
-
Responsiveness of the P4, Patient Specific Functional Scale 2.0, Satisfaction and Recovery Index, and SF-12 in Patients With Musculoskeletal Disorders.Cureus. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):e71571. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71571. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39553117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Falla D, Jull G, Hodges PW. Feedforward activity of the cervical flexor muscles during voluntary arm movements is delayed in chronic neck pain. Exp Brain Res. 2004;157:43–8. - PubMed
-
- Falla DL, Jull GA, Hodges PW. Patients with neck pain demonstrate reduced electromyographic activity of the deep cervical flexor muscles during performance of the craniocervical flexion test. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:2108–14. - PubMed
-
- Schomacher J, Farina D, Lindstroem R, Falla D. Chronic trauma-induced neck pain impairs the neural control of the deep semispinalis cervicis muscle. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123:1403–8. - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom R, Schomacher J, Farina D, Rechter L, Falla D. Association between neck muscle coactivation, pain, and strength in women with neck pain. Man Ther. 2011;16:80–6. - PubMed
-
- Falla D, Farina D, Graven-Nielsen T. Experimental muscle pain results in reorganization of coordination among trapezius muscle subdivisions during repetitive shoulder flexion. Exp Brain Res. 2007;178:385–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
