Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Plasmids Allow Scalable, PCR-Mediated DNA Manipulation and Near-Zero Background Cloning
- PMID: 27956856
- PMCID: PMC5151216
- DOI: 10.17113/ftb.54.03.16.4230
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Plasmids Allow Scalable, PCR-Mediated DNA Manipulation and Near-Zero Background Cloning
Abstract
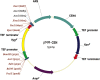
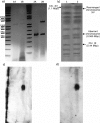
We have constructed two plasmids that can be used for cloning as templates for PCR- -based gene disruption, mutagenesis and the construction of DNA chromosome translocation cassettes. To our knowledge, these plasmids are the first vectors that confer resistance to ampicillin, kanamycin and hygromycin B in bacteria, and to geneticin (G418) and hygromycin B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae simultaneously. The option of simultaneously using up to three resistance markers provides a highly stringent control of recombinant selection and the almost complete elimination of background resistance, while unique restriction sites allow easy cloning of chosen genetic material. Moreover, we successfully used these new vectors as PCR templates for the induction of chromosome translocation in budding yeast by the bridge-induced translocation system. Cells in which translocation was induced carried chromosomal rearrangements as expected and exhibited resistance to both, G418 and hygromycin B. These features make our constructs very handy tools for many molecular biology applications.
Keywords: DNA manipulation; functional analysis; gene knock-out; multi-marker vectors; multiple-antibiotic resistance; yeast.
Figures


Similar articles
-
New and Redesigned pRS Plasmid Shuttle Vectors for Genetic Manipulation of Saccharomycescerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 May;2(5):515-26. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.001917. Epub 2012 May 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 22670222 Free PMC article.
-
Hygromycin B and apramycin antibiotic resistance cassettes for use in Campylobacter jejuni.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 21;9(4):e95084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095084. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24751825 Free PMC article.
-
Direct selection of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the antibiotic G418 following transformation with a DNA vector carrying the kanamycin-resistance gene of Tn903.Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):243-52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90194-4. Gene. 1983. PMID: 6323263
-
System of centromeric, episomal, and integrative vectors based on drug resistance markers for Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biotechniques. 2006 Jan;40(1):73-8. doi: 10.2144/000112040. Biotechniques. 2006. PMID: 16454043
-
Hygromycin B resistance as dominant selectable marker in yeast.Curr Genet. 1984 Jul;8(5):353-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00419824. Curr Genet. 1984. PMID: 24177815
Cited by
-
Post-translocational adaptation drives evolution through genetic selection and transcriptional shift in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Curr Genet. 2017 May;63(2):281-292. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0635-x. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27491680
References
-
- Casali N, Preston A, editors. E. coli plasmid vectors: methods and applications. New York, NY, USA: Humana Press; 2003.
-
- Walsh C. Antibiotics: actions, origins, resistance. Washington DC, USA: ASM Press; 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
