Focal Impulse And Rotor Mapping (FIRM): Conceptualizing And Treating Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 27957100
- PMCID: PMC5135257
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.1103
Focal Impulse And Rotor Mapping (FIRM): Conceptualizing And Treating Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
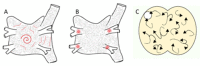
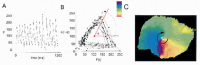
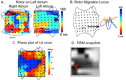
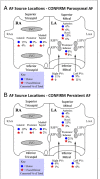
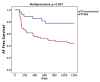
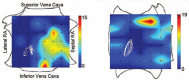
Current approaches for the ablation of atrial fibrillation are often effective, but only partially rooted in mechanistic understanding. Accordingly, they are unable to predict whether a given patient will or will not do well, or which lesions sets should or should not be performed - in any given patient. This goal would require clearer mechanistic definition of what sustains AF after it has been triggered (i.e. electrophysiological substrates). There are two schools of thought. The first proposes disorganized activity that self-sustains with no 'driver', and the second describes drivers that then cause disorganization. Interestingly, these mechanisms can be separated in human studies by mapping approach - proponents of the disorganized hypothesis studying small atrial areas at high resolution, and proponents of the driver model studying wide fields-of-view at varying resolutions. Focal impulse and rotor modulation (FIRM) mapping combines a wide field of view with physiologically based signal filtering and phase analysis, and has revealed that human AF is often sustained by rotors. In the CONFIRM Trial, targeting stable AF rotors/sources for ablation improved the single-procedure efficacy for paroxysmal and persistent AF over conventional ablation alone, as now confirmed by independent laboratories. FIRM mapping gives a mechanistic foundation to predict whether any selected lesions should intersect AF sources in any given patient and which mechanisms may cause recurrence. Rotors of varying characteristics have now been shown by many groups. These insights have reinvigorated interest in AF mapping, and rationalizing these findings will likely translate into improved therapy for our patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment of atrial fibrillation by the ablation of localized sources: CONFIRM (Conventional Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation With or Without Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation) trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Aug 14;60(7):628-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.05.022. Epub 2012 Jul 18. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22818076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-invasive identification of stable rotors and focal sources for human atrial fibrillation: mechanistic classification of atrial fibrillation from the electrocardiogram.Europace. 2013 Sep;15(9):1249-58. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut038. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Europace. 2013. PMID: 23449925 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of rotors and focal sources for human atrial fibrillation: focal impulse and rotor mapping (FIRM) of AF sources and fibrillatory conduction.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014 Dec;25(12):1284-92. doi: 10.1111/jce.12559. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014. PMID: 25263408
-
Mapping and ablating stable sources for atrial fibrillation: summary of the literature on Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation (FIRM).J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2014 Sep;40(3):237-44. doi: 10.1007/s10840-014-9889-8. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24647673 Review.
-
The role of rotors in atrial fibrillation.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Feb;7(2):142-51. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.11.15. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 25713729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dispersion electrogram detection with an artificial intelligence software in redo paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation.HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2023 Oct 9;9(12):948-953. doi: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2023.10.006. eCollection 2023 Dec. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38204832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Atrial fibrillation observed on surface ECG can be atrial flutter or atrial tachycardia.J Electrocardiol. 2018 Nov-Dec;51(6S):S67-S71. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Electrocardiol. 2018. PMID: 30029778 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter Ablation in Persistent AF, the Evolution towards a More Pragmatic Strategy.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 8;10(18):4060. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184060. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrogram Morphology Recurrence for Mapping Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Initial vs Redo Catheter Ablation.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2023 Apr;9(4):526-540. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2022.11.003. Epub 2023 Jan 18. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2023. PMID: 36669899 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond pulmonary vein isolation for persistent atrial fibrillation: sequential high-resolution mapping to guide ablation.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2022 Oct;65(1):53-62. doi: 10.1007/s10840-021-01115-7. Epub 2022 Jan 8. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35000099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chugh Sumeet S, Havmoeller Rasmus, Narayanan Kumar, Singh David, Rienstra Michiel, Benjamin Emelia J, Gillum Richard F, Kim Young-Hoon, McAnulty John H, Zheng Zhi-Jie, Forouzanfar Mohammad H, Naghavi Mohsen, Mensah George A, Ezzati Majid, Murray Christopher J L. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 2014 Feb 25;129 (8):837–47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ganesan Anand N, Shipp Nicholas J, Brooks Anthony G, Kuklik Pawel, Lau Dennis H, Lim Han S, Sullivan Thomas, Roberts-Thomson Kurt C, Sanders Prashanthan. Long-term outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013 Mar 18;2 (2):e004549. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cox J L, Canavan T E, Schuessler R B, Cain M E, Lindsay B D, Stone C, Smith P K, Corr P B, Boineau J P. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. II. Intraoperative electrophysiologic mapping and description of the electrophysiologic basis of atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1991 Mar;101 (3):406–26. - PubMed
-
- Allessie M A, Bonke F I, Schopman F J. Circus movement in rabbit atrial muscle as a mechanism of trachycardia. Circ. Res. 1973 Jul;33 (1):54–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
