Vagus Nerve Stimulation Enhances Extinction of Conditioned Fear in Rats and Modulates Arc Protein, CaMKII, and GluN2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in the Basolateral Amygdala
- PMID: 27957346
- PMCID: PMC5120198
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4273280
Vagus Nerve Stimulation Enhances Extinction of Conditioned Fear in Rats and Modulates Arc Protein, CaMKII, and GluN2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in the Basolateral Amygdala
Abstract
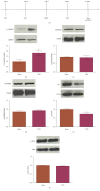
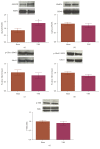
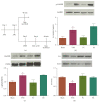
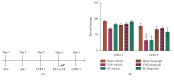
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) enhances the consolidation of extinction of conditioned fear. High frequency stimulation of the infralimbic cortex (IL) produces long-term potentiation in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) in rats given VNS-paired extinction training, whereas the same stimulation produces long-term depression in sham-treated rats. The present study investigated the state of synaptic plasticity-associated proteins in the BLA that could be responsible for this shift. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were separated into 4 groups: auditory fear conditioning only (fear-conditioned); fear conditioning + 20 extinction trials (extended-extinction); fear conditioning + 4 extinction trials paired with sham stimulation (sham-extinction); fear conditioning + 4 extinction trials paired with VNS (VNS-extinction). Freezing was significantly reduced in extended-extinction and VNS-extinction rats. Western blots were used to quantify expression and phosphorylation state of synaptic plasticity-associated proteins such as Arc, CaMKII, ERK, PKA, and AMPA and NMDA receptors. Results show significant increases in GluN2B expression and phosphorylated CaMKII in BLA samples from VNS- and extended-extinction rats. Arc expression was significantly reduced in VNS-extinction rats compared to all groups. Administration of the GluN2B antagonist ifenprodil immediately after fear extinction training blocked consolidation of extinction learning. Results indicate a role for BLA CaMKII-induced GluN2B expression and reduced Arc protein in VNS-enhanced extinction.
Conflict of interest statement
Amanda C. Alvarez-Dieppa, Kimberly Griffin, and Sheridan Cavalier have no competing interests, and Christa K. McIntyre is an author of the following patents: “Timing Control for Paired Plasticity” whose inventors are Michael Kilgard, Lawrence Cauller, Navzer Engineer, Christa McIntyre, and Will Rosellini; “Methods for Enhancing Exposure Therapy using Vagus Nerve Stimulation” whose inventors are Christa McIntyre, Navzer Engineer, and Michael Kilgard; “System, Methods and Devices for Treating Tinnitus” whose inventors are Michael Kilgard, Navzer Engineer, and Christa McIntyre.
Figures
References
-
- Blechert J., Michael T., Vriends N., Margraf J., Wilhelm F. H. Fear conditioning in posttraumatic stress disorder: evidence for delayed extinction of autonomic, experiential, and behavioural responses. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2007;45(9):2019–2033. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2007.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clark K. B., Smith D. C., Hassert D. L., Browning R. A., Naritoku D. K., Jensen R. A. Posttraining electrical stimulation of vagal afferents with concomitant vagal efferent inactivation enhances memory storage processes in the rat. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 1998;70(3):364–373. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1998.3863. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

