Molecular Liver Cancer Prevention in Cirrhosis by Organ Transcriptome Analysis and Lysophosphatidic Acid Pathway Inhibition
- PMID: 27960085
- PMCID: PMC5161110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.004
Molecular Liver Cancer Prevention in Cirrhosis by Organ Transcriptome Analysis and Lysophosphatidic Acid Pathway Inhibition
Abstract
Cirrhosis is a milieu that develops hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the second most lethal cancer worldwide. HCC prediction and prevention in cirrhosis are key unmet medical needs. Here we have established an HCC risk gene signature applicable to all major HCC etiologies: hepatitis B/C, alcohol, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. A transcriptome meta-analysis of >500 human cirrhotics revealed global regulatory gene modules driving HCC risk and the lysophosphatidic acid pathway as a central chemoprevention target. Pharmacological inhibition of the pathway in vivo reduced tumors and reversed the gene signature, which was verified in organotypic ex vivo culture of patient-derived fibrotic liver tissues. These results demonstrate the utility of clinical organ transcriptome to enable a strategy, namely, reverse-engineering precision cancer prevention.
Keywords: cancer chemoprevention; gene signature; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognostic prediction; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
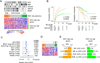

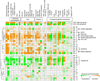
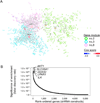


References
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
-
- Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Pinna F, Frau M, Tomasi ML, Sini M, Simile MM, Bonelli P, Muroni MR, Seddaiu MA, et al. SKP2 and CKS1 promote degradation of cell cycle regulators and are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1816–1826. e1811–e1810. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

