Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle
- PMID: 27965149
- PMCID: PMC5325811
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.006
Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle
Abstract
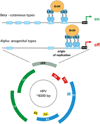
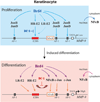
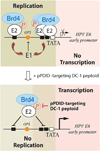
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (Brd4) is a cellular chromatin-binding factor and transcriptional regulator that recruits sequence-specific transcription factors and chromatin modulators to control target gene transcription. Papillomaviruses (PVs) have evolved to hijack Brd4's activity in order to create a facilitating environment for the viral life cycle. Brd4, in association with the major viral regulatory protein E2, is involved in multiple steps of the PV life cycle including replication initiation, viral gene transcription, and viral genome segregation and maintenance. Phosphorylation of Brd4, regulated by casein kinase II (CK2) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), is critical for viral gene transcription as well as E1- and E2-dependent origin replication. Thus, pharmacological agents regulating Brd4 phosphorylation and inhibitors blocking phospho-Brd4 functions are promising candidates for therapeutic intervention in treating human papillomavirus (HPV) infections as well as associated disease.
Keywords: Brd4; E2 protein; Papillomavirus life cycle; Papillomavirus replication; Papillomavirus transcription.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abbate EA, Voitenleitner C, Botchan MR. Structure of the papillomavirus DNA-tethering complex E2:Brd4 and a peptide that ablates HPV chromosomal association. Mol. Cell. 2006;24(6):877–889. - PubMed
-
- Akgul B, Garcia-Escudero R, Ekechi C, Steger G, Navsaria H, Pfister H, Storey A. The E2 protein of human papillomavirus type 8 increases the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human keratinocytes and organotypic skin cultures. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011;200(2):127–135. - PubMed
-
- Behren A, Simon C, Schwab RM, Loetzsch E, Brodbeck S, Huber E, Stubenrauch F, Zenner HP, Iftner T. Papillomavirus E2 protein induces expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/activator protein-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2005;65(24):11613–11621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

