Effects of platelet-rich plasma and triamcinolone acetonide on interleukin-1ß-stimulated human rotator cuff-derived cells
- PMID: 27965219
- PMCID: PMC5227058
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.512.2000582
Effects of platelet-rich plasma and triamcinolone acetonide on interleukin-1ß-stimulated human rotator cuff-derived cells
Abstract
Objectives: Triamcinolone acetonide (TA) is widely used for the treatment of rotator cuff injury because of its anti-inflammatory properties. However, TA can also produce deleterious effects such as tendon degeneration or rupture. These harmful effects could be prevented by the addition of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), however, the anti-inflammatory and anti-degenerative effects of the combined use of TA and PRP have not yet been made clear. The objective of this study was to determine how the combination of TA and PRP might influence the inflammation and degeneration of the rotator cuff by examining rotator cuff-derived cells induced by interleukin (IL)-1ß.
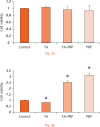
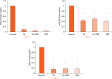
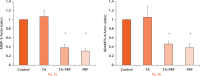
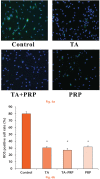
Methods: Rotator cuff-derived cells were seeded under inflammatory stimulation conditions (with serum-free medium with 1 ng/ml IL-1ß for three hours), and then cultured in different media: serum-free (control group), serum-free + TA (0.1mg/ml) (TA group), serum-free + 10% PRP (PRP group), and serum-free + TA (0.1mg/ml) + 10% PRP (TA+PRP group). Cell morphology, cell viability, and expression of inflammatory and degenerative mediators were assessed.
Results: Exposure to TA significantly decreased cell viability and changed the cell morphology; these effects were prevented by the simultaneous administration of PRP. Compared with the control group, expression levels of inflammatory genes and reactive oxygen species production were reduced in the TA, PRP, and TA+PRP groups. PRP significantly decreased the expression levels of degenerative marker genes.
Conclusions: The combination of TA plus PRP exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-degenerative effects on rotator cuff-derived cells stimulated by IL-1ß. This combination has the potential to relieve the symptoms of rotator cuff injury.Cite this article: T. Muto, T. Kokubu, Y. Mifune, A. Inui, R. Sakata, Y. Harada, F. Takase, M. Kurosaka. Effects of platelet-rich plasma and triamcinolone acetonide on interleukin-1ß-stimulated human rotator cuff-derived cells. Bone Joint Res 2016;5:602-609. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.512.2000582.
Keywords: Anti-degeneration; Anti-inflammation; Platelet-rich plasma; Rotator cuff-derived cell; Triamcinolone acetonide.
© 2016 Muto et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflicts of Intrest: None declared
Figures

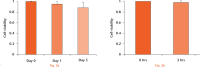
Similar articles
-
Platelet-rich plasma protects rotator cuff-derived cells from the deleterious effects of triamcinolone acetonide.J Orthop Res. 2013 Jun;31(6):976-82. doi: 10.1002/jor.22301. Epub 2012 Dec 31. J Orthop Res. 2013. PMID: 23280560
-
Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma With Concomitant Use of a Corticosteroid on Tenocytes From Degenerative Rotator Cuff Tears in Interleukin 1β-Induced Tendinopathic Conditions.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Apr;45(5):1141-1150. doi: 10.1177/0363546516681294. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28061032
-
Allogenic Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Rotator Cuff Disease: A Bench and Bed Study.Am J Sports Med. 2018 Nov;46(13):3142-3154. doi: 10.1177/0363546518800268. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Am J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 30311796
-
Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a meta-analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015 Dec;24(12):1852-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.035. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015. PMID: 26456434 Review.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Reduces Retear Rates After Arthroscopic Repair of Small- and Medium-Sized Rotator Cuff Tears but Is Not Cost-Effective.Am J Sports Med. 2015 Dec;43(12):3071-6. doi: 10.1177/0363546515572777. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Am J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25767267 Review.
Cited by
-
PRP as a modulator of inflammation in FLS of RA patients by regulation of galectins and TGF-β1.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 3;10(1):e24036. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24036. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268610 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Oxidative Stress in Acute Tendon Injury and Degenerative Tendinopathy-A Target for Intervention.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 25;23(7):3571. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073571. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-articular platelet-rich plasma vs corticosteroids in the treatment of moderate knee osteoarthritis: a single-center prospective randomized controlled study with a 1-year follow up.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Jul 10;15(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01753-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32650801 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Analysis of Platelet-rich Plasma Effect on Tenocytes from Normal Human Rotator Cuff Tendon and Human Rotator Cuff Tendon with Degenerative Tears.Clin Shoulder Elb. 2018 Mar 1;21(1):3-14. doi: 10.5397/cise.2018.21.1.3. eCollection 2018 Mar. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2018. PMID: 33330145 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Use of Triamcinolone and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Equine Metacarpophalangeal Joint Osteoarthritis Treatments: An In Vivo and In Vitro Study.Animals (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;14(24):3645. doi: 10.3390/ani14243645. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blair B, Rokito AS, Cuomo F, Jarolem K, Zuckerman JD. Efficacy of injections of corticosteroids for subacromial impingement syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1996;78-A:1685-1689. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez CM, Litchfield R, Jackowski D, Griffin S, Kirkley A. A prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial comparing subacromial injection of betamethasone and xylocaine to xylocaine alone in chronic rotator cuff tendinosis. Am J Sports Med 2005;33:255-262. - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Dobrow R, Neiman R, Whiting-O’Keefe Q, Seaman WE. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the treatment of the painful shoulder. Arthritis Rheum 1987;30:1040-1045. - PubMed
-
- Adebajo AO, Nash P, Hazleman BL. A prospective double blind dummy placebo controlled study comparing triamcinolone hexacetonide injection with oral diclofenac 50 mg TDS in patients with rotator cuff tendinitis. J Rheumatol 1990;17:1207-1210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

