Trends in Weight-for-Length Among Infants in WIC From 2000 to 2014
- PMID: 27965380
- PMCID: PMC5359001
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-2034
Trends in Weight-for-Length Among Infants in WIC From 2000 to 2014
Abstract
Objectives: To describe the prevalence and secular trends of high weight-for-length among infants (ages, 3-23 months) in the biennial US Department of Agriculture Women, Infants, and Children Program and Participants Characteristic (WIC-PC) Survey from 2000 through 2014 (n = 16 927 120).
Methods: Weight-for-length was considered to be "high" if it was ≥2 SDs above the sex- and age-specific median in the World Health Organization growth standards. Poisson regression was used to calculate adjusted prevalence ratios.
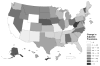
Results: The overall prevalence of high weight-for-length increased from 13.4% in 2000 to 14.5% in 2004, remained constant until 2010, and then decreased by >2 percentage points (to 12.3%) through 2014. The prevalence of high weight-for-length was associated with sex (higher among boys), race-ethnicity (highest among American Indians/Alaskan Natives), and with both age (positive) and family income (inverse). The secular trends, however, were fairly similar within categories of these variables. From 2010 to 2014, the prevalence of high weight-for-length decreased in 40 states and 3 (of 5) US territories, with the largest decreases seen in Puerto Rico (-9 percentage points) and Kentucky (-7 percentage points), and the largest increase (+2 percentage points) seen in West Virginia.
Conclusions: Although the current results cannot be considered representative of infants in the populations, the prevalence of a high weight-for-length has decreased among infants in WIC-PC since 2010. These decreases were similar across categories of most characteristics, but there were substantial differences across jurisdictions, possibly reflecting differences in policy and local programs that target maternal and infant health.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children participation and infants' growth and health: a multisite surveillance study.Pediatrics. 2004 Jul;114(1):169-76. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.1.169. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15231924
-
Comparing Weight-for-Length Status of Young Children in Two Infant Feeding Programs.Matern Child Health J. 2016 Dec;20(12):2518-2526. doi: 10.1007/s10995-016-2077-y. Matern Child Health J. 2016. PMID: 27485490
-
Changes in High Weight-for-Length among Infants Enrolled in Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children during 2010-2018.Child Obes. 2021 Sep;17(6):408-419. doi: 10.1089/chi.2021.0055. Epub 2021 May 6. Child Obes. 2021. PMID: 33960827 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
USDA Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children (WIC) Vendor Criteria: An Examination of US Administrative Agency Variations.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 29;18(7):3545. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073545. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33805495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Feeding Infants and Toddlers Study (FITS) 2016: Moving Forward.J Nutr. 2018 Sep 1;148(suppl_3):1575S-1580S. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxy159. J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30247582 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cultural influences on infant and toddler feeding among low-income Latinx mothers.Matern Child Nutr. 2022 Oct;18(4):e13342. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13342. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Matern Child Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35702987 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Controlled Trial to Prevent Infant Overweight in a High-Risk Population.Acad Pediatr. 2018 Apr;18(3):324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Acad Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29277462 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Food and Beverage Intake From 12 to 23 Months by WIC Status.Pediatrics. 2019 Mar;143(3):e20182274. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2274. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Pediatrics. 2019. PMID: 30733238 Free PMC article.
-
Lactose-reduced infant formula with corn syrup solids and obesity risk among participants in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Oct 6;116(4):1002-1009. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac173. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35998087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288(14):1728–1732. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Flegal KM. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2015;(219):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo A, Monasta L, Stamatakis E, et al. Overweight and obesity in infants and pre-school children in the European Union: a review of existing data. Obes Rev. 2010;11(5):389–398. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

