Fox transcription factors: from development to disease
- PMID: 27965437
- PMCID: PMC5201025
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.112672
Fox transcription factors: from development to disease
Abstract
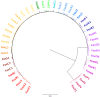
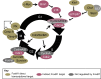
Forkhead box (Fox) transcription factors are evolutionarily conserved in organisms ranging from yeast to humans. They regulate diverse biological processes both during development and throughout adult life. Mutations in many Fox genes are associated with human disease and, as such, various animal models have been generated to study the function of these transcription factors in mechanistic detail. In many cases, the absence of even a single Fox transcription factor is lethal. In this Primer, we provide an overview of the Fox family, highlighting several key Fox transcription factor families that are important for mammalian development.
Keywords: Foregut development; Forkhead; Fox; Language acquisition; Pioneer factors; Transcription factors.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Adams J., Palombella V. J., Sausville E. A., Johnson J., Destree A., Lazarus D. D., Maas J., Pien C. S., Prakash S. and Elliott P. J. (1999). Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 59, 2615-2622. - PubMed
-
- Ang S. L., Wierda A., Wong D., Stevens K. A., Cascio S., Rossant J. and Zaret K. S. (1993). The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development 119, 1301-1315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

