Efficacy of Capecitabine Plus Oxaliplatin Combination Chemotherapy for Advanced Pancreatic Cancer after Failure of First-Line Gemcitabine-Based Therapy
- PMID: 27965478
- PMCID: PMC5347656
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl16307
Efficacy of Capecitabine Plus Oxaliplatin Combination Chemotherapy for Advanced Pancreatic Cancer after Failure of First-Line Gemcitabine-Based Therapy
Abstract
Background/aims: Second-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) that progresses following gemcitabine-based treatment has not been established. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of second-line combination chemotherapy with capecitabine and oxaliplatin (XELOX) in these patients.
Methods: Between August 2011 and May 2014, all patients who received at least one cycle of XELOX (capecitabine, 1,000 mg/m2 twice daily for 14 days; oxaliplatin, 130 mg/m2 on day 1 of a 3-week cycle) combination chemotherapy for unresectable or recurrent PDAC were retrospectively recruited. The response was evaluated every 9 weeks, and the tumor response rate, progression-free survival and overall survival, and adverse events were assessed.
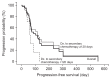
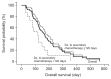
Results: Sixty-two patients were included; seven patients (11.3%) had a partial tumor response, and 20 patients (32.3%) had stable disease. The median progression-free and overall survival were 88 days (range, 35.1 to 140.9 days) and 158 days (range, 118.1 to 197.9 days), respectively. Patients who remained stable longer with frontline therapy (≥120 days) exhibited significantly longer progression-free and overall survival. The most common grade 3 to 4 adverse events in patients were vomiting (8.1%) and anorexia (6.5%). There was one treatment-related mortality caused by severe neutropenia and typhlitis.
Conclusions: Second-line XELOX combination chemotherapy demonstrated an acceptable response and survival rate in patients with advanced PDAC who had failed gemcitabine-based chemotherapy.
Keywords: Capecitabine; Carcinoma, pancreatic ductal; Oxaliplatin; Salvage therapy; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combining capecitabine, oxaliplatin, and gemcitabine (XELOXGEM) for colorectal carcinoma patients pretreated with irinotecan: a multicenter phase I/II trial.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;69(1):91-7. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1668-y. Epub 2011 May 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21607556 Clinical Trial.
-
XELOX vs. FOLFOX4 as second line chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer.Hepatogastroenterology. 2012 Nov-Dec;59(120):2635-9. doi: 10.5754/hge12181. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22534542
-
Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (CapOx) versus capecitabine plus gemcitabine (CapGem) versus gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin (mGemOx): final results of a multicenter randomized phase II trial in advanced pancreatic cancer.Ann Oncol. 2008 Feb;19(2):340-7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm467. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Ann Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17962204 Clinical Trial.
-
Current Standard and Future Perspectives in First- and Second-Line Treatment of Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Digestion. 2016;94(1):44-9. doi: 10.1159/000447739. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Digestion. 2016. PMID: 27438590 Review.
-
Adjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: state of the art and future perspectives.Curr Opin Oncol. 2020 Jul;32(4):356-363. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000639. Curr Opin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32541325 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Clinical Predictive Factors Affecting the Outcome of Second-Line Chemotherapy for Gemcitabine-Refractory Advanced Pancreatic Cancer.Gut Liver. 2020 Jan 15;14(1):135-143. doi: 10.5009/gnl18419. Gut Liver. 2020. PMID: 30974927 Free PMC article.
-
DBDx-based drug combinations show highly potent therapeutic efficacy against human pancreatic cancer xenografts in athymic mice.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Aug 2;21(8):749-757. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1776580. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32644888 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of the combination of nano-liposomal irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin in advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: post-approval clinic experience.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Apr;12(2):464-473. doi: 10.21037/jgo-20-338. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34012640 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Pancreatic Cancer: Implications in Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 24;11(11):1627. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111627. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31652904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish model of KRAS-initiated pancreatic cancer.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2018 Oct 8;22(6):353-359. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2018.1530301. eCollection 2018. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 30533257 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

