Laryngeal Sensitivity in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 27965622
- PMCID: PMC5124602
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00212
Laryngeal Sensitivity in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
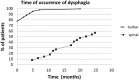
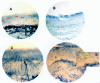
Recent studies have shown the involvement of the sensory nervous system in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The aim of our study was to investigate the correlation between the laryngeal sensitivity deficit and the type of ALS onset (bulbar or spinal) in a large series of 114 consecutive ALS patients. Participants were subdivided into two groups, bulbar and spinal ALS, according to the clinical onset of disease and submitted to a clinical and instrumental evaluation of swallowing, including a fiber-optic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing. Dysphagia severity was scored using the Penetration-Aspiration Scale (PAS) and the Pooling score (P-score). In addition, three patients with laryngeal sensitivity deficit were submitted to a laryngeal biopsy to assess the status of the sensory innervation. All patients showed a normal glottal closure during phonation and volitional cough. Fifty-six subjects (49%), 14 spinal- and 42 bulbar-onset ALS, showed dysphagia at the first clinical observation (PAS score >1; P-score >5). Dysphagia resulted more frequently in bulbar-onset ALS (P < 0.01). Thirty-eight (33%) patients had a sensory deficit of the larynx. The sensory deficit of the larynx was significantly more frequent in bulbar-onset ALS (P < 0.01). The sensory deficit of the larynx among dysphagic patients was also significantly more frequent in bulbar-onset ALS (P = 0.02). Several abnormalities were found in all three subjects who underwent a laryngeal biopsy: in one patient, no intraepidermal fiber was found; in the other two, the fibers showed morphological changes. Our observations are important to consider for assessment and management of dysphagia in patients with ALS.
Keywords: PGP 9.5; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; deglutition disorders; larynx; sensory nerve endings.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

