Doppler ultrasound in kidney diseases: a key parameter in clinical long-term follow-up
- PMID: 27965714
- PMCID: PMC5126008
- DOI: 10.1007/s40477-016-0201-x
Doppler ultrasound in kidney diseases: a key parameter in clinical long-term follow-up
Abstract
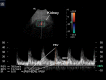
Doppler ultrasound has been extensively used in detecting reno-vascular diseases, showing to be a non-invasive, safe, low cost and repeatable tool. The Renal Resistive Index (RRI) [(peak systolic velocity - end diastolic velocity)/peak systolic velocity] is a semi-quantitative index derived by Doppler evaluation of renal vascular bed. Normally RRI is in the range of 0.47-0.70, it increases with aging and, usually, it shows a difference between the two kidneys less than 5-8 %. RRI is an important prognostic marker in chronic kidney diseases (CKD), both in diabetic and non-diabetic kidney diseases, because, in longitudinal prospective studies, it significantly correlated with hemodynamic (ABPM, SBP, DBP, pulse pressure) and histopathological parameters (glomerular sclerosis, arteriolosclerosis, interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy, interstitial infiltration). In acute kidney injury (AKI) RI is a valid tool in differentiating between pre-renal and renal failure and in predicting renal response to vaso-active agents. In addition a RRI >0.74 can predict the onset of AKI in septic patients. Renal Resistive Index is a useful marker in allograft diseases because it has been widely showed a correlation with histological lesions during worsening of renal function, both in acute rejection and in chronic allograft nephropathy. Recent studies suggest its role in the risk of new onset diabetes after transplantation and it could be one of the parameters to evaluate to shift or withdrawal immunological and/or hypertensive therapy.
La Metodica Color Doppler è stata diffusamente utilizzata per evidenziare patologie nefrovascolari in relazione alle caratteristiche di non invasività, sicurezza, basso costo e ripetibilità della stessa. L'indice di resistenza renale (RRI) [(Picco di velocità sistolica - Velocità telediastolica)/ Picco di velocità sistolica] è un indice semiquantitativo derivato dalla valutazione Doppler del letto vascolare renale.Normalmente il valore del RRI è nel range di 0,47- 0,70, aumentando con l'età, e usualmente, è presente una differenza tra i due reni inferiore al 5-8%. RRI è un importante marker prognostico nelle patologie renali croniche (CKD), sia diabetiche che non-diabetiche, poichè, in studi prospettici longitudinali, esso correla significativamente con parametri emodinamici (ABPM, Pressione Sistolica, pressione Diastolica, Pressione di Polso) e istopatologici (glomerulosclerosi, arteriolosclerosi, fibrosi interstiziale/atrofia tubulare e infiltrato interstiziale).Nel Danno Renale Acuto (AKI) RI è un valido strumento nel distinguere l'insufficienza acuta pre-renale da quella renale e nel predire la risposta renale agli agenti vasoattivi. Inoltre un valore di RRI >0,74 può predire la comparsa di AKI nei pazienti affetti da sepsi.RRI è un marker utile nelle patologie del rene trapiantato, perchè è stata ampiamente dimostrata una correlazione con lesioni istologiche nel contesto di un peggioramento della funzione renale, sia nel rigetto acuto che nella nefropatia cronica del trapianto. Studi recenti suggeriscono un suo ruolo nel predire la comparsa del diabete di nuova insorgenza dopo il trapianto (NODAT) e potrebbe essere uno dei parametri da valutare nella sostituzione o nella sospensione della terapia immunologica e/o ipertensiva.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetic nephropathy; Renal resistive index; Renal transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards Conflict of interests The authors declare that they have no competing or conflicting interests. Informed consent For this type of study formal consent is not required. Human and animal studies The study described in this article does not contain studies with animal and human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- National Kidney Foundation K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(Suppl 1):266. - PubMed
-
- Darmon M, Schnell D, Zeni F. Doppler-based renal resistive index: a comprehensive review. In: Vincent JL, editor. Yearbook of intensive care and emergency medicine. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. pp. 331–338.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical