Acute corticospinal and spinal modulation after whole body vibration
- PMID: 27973385
- PMCID: PMC5259574
Acute corticospinal and spinal modulation after whole body vibration
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to investigate neural effects of acute whole body vibration (WBV) on lower limb muscles regarding corticospinal and spinal excitability.
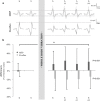
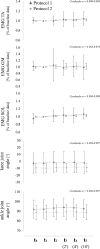
Methods: In 44 healthy subjects (16 f/ 28 m), motor evoked potentials (MEP) and H-reflexes in m. soleus (SOL) and gastrocnemius medialis (GM) were elicited before (t1), immediately after (t2), 2 (t3), 4 (t4) and 10 min after (t5) WBV.
Results: After WBV, MEP amplitudes were significantly increased in SOL (t2+15±30%, t3+22±32%, t4+15±35%, t5+20±30%, P<0.05), but not in GM (t2+32±62%, t3+9±35%, t4+8±36%, t5+22±47%; P=0.07). Contrarily, H-reflexes were significantly reduced in SOL (t2-19±28%, t3-21±22%, t4-20±21%, t5-14±28%, P<0.05) and GM (t2-14±37%, t3-16±25%, t4-18±29%, t5-16±28%, P<0.05).
Conclusions: A temporary sustained enhancement of corticospinal excitability concomitant with spinal inhibition after WBV points towards persisting neural modulation in the central nervous system. This could indicate greater neural modulation over M1 and descending pathways, while the contribution of spinal pathways is reduced.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cochrane DJ. Vibration exercise: the potential benefits. Int J Sports Med. 2011;32(2):75–99. - PubMed
-
- Rittweger J. Vibration as an exercise modality: how it may work, and what its potential might be. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(5):877–904. - PubMed
-
- Roelants M, Delecluse C, Verschueren SM. Whole-body-vibration training increases knee-extension strength and speed of movement in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(6):901–08. - PubMed
-
- Stark C, Nikopoulou-Smyrni P, Stabrey A, Semler O, Schoenau E. Effect of a new physiotherapy concept on bone mineral density, muscle force and gross motor function in children with bilateral cerebral palsy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2010;10(2):151–58. - PubMed
