Tau Prion Strains Dictate Patterns of Cell Pathology, Progression Rate, and Regional Vulnerability In Vivo
- PMID: 27974162
- PMCID: PMC5392364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.055
Tau Prion Strains Dictate Patterns of Cell Pathology, Progression Rate, and Regional Vulnerability In Vivo
Abstract
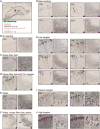
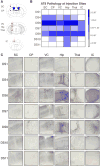
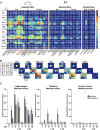
Tauopathies are neurodegenerative disorders that affect distinct brain regions, progress at different rates, and exhibit specific patterns of tau accumulation. The source of this diversity is unknown. We previously characterized two tau strains that stably maintain unique conformations in vitro and in vivo, but did not determine the relationship of each strain to parameters that discriminate between tauopathies such as regional vulnerability or rate of spread. We have now isolated and characterized 18 tau strains in cells based on detailed biochemical and biological criteria. Inoculation of PS19 transgenic tau (P301S) mice with these strains causes strain-specific intracellular pathology in distinct cell types and brain regions, and induces different rates of network propagation. In this system, strains alone are sufficient to account for diverse neuropathological presentations, similar to those that define human tauopathies. Further study of these strains can thus establish a structural logic that governs these biological effects.
Keywords: cell model; prion; prion-like; seeding activity; strain; tau; tau pathology; tauopathy; transcellular propagation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Straining the brain.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Nov 17;17(12):738. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.161. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27853142 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barghorn S, Zheng-Fischhöfer Q, Ackmann M, Biernat J, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E. Structure, Microtubule Interactions, and Paired Helical Filament Aggregation by Tau Mutants of Frontotemporal Dementias †. Biochemistry. 2000;39:11714–11721. - PubMed
-
- Boluda S, Iba M, Zhang Bin, Raible KM, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ. Differential induction and spread of tau pathology in young PS19 tau transgenic mice following intracerebral injections of pathological tau from Alzheimer's disease or corticobasal degeneration brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2015;129:221–237. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

