Analytical ingredient content and variability of adult multivitamin/mineral products: national estimates for the Dietary Supplement Ingredient Database
- PMID: 27974309
- PMCID: PMC5267296
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.116.134544
Analytical ingredient content and variability of adult multivitamin/mineral products: national estimates for the Dietary Supplement Ingredient Database
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to Andrews KW, Roseland JM, Gusev PA, Palachuvattil J, Dang PT, Savarala S, Han F, Pehrsson PR, Douglass LW, Dwyer JT, Betz JM, Saldanha LG, Bailey RL. Analytical ingredient content and variability of adult multivitamin/mineral products: national estimates for the Dietary Supplement Ingredient Database. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017 Feb;105(2):526-539. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.134544. Epub 2016 Dec 14.Am J Clin Nutr. 2020 Apr 1;111(4):920. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqz278. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32266396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Multivitamin/mineral products (MVMs) are the dietary supplements most commonly used by US adults. During manufacturing, some ingredients are added in amounts exceeding the label claims to compensate for expected losses during the shelf life. Establishing the health benefits and harms of MVMs requires accurate estimates of nutrient intake from MVMs based on measures of actual rather than labeled ingredient amounts.
Objectives: Our goals were to determine relations between analytically measured and labeled ingredient content and to compare adult MVM composition with Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) and Tolerable Upper Intake Levels.
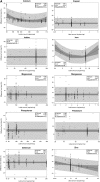
Design: Adult MVMs were purchased while following a national sampling plan and chemically analyzed for vitamin and mineral content with certified reference materials in qualified laboratories. For each ingredient, predicted mean percentage differences between analytically obtained and labeled amounts were calculated with the use of regression equations.
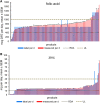
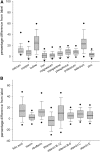
Results: For 12 of 18 nutrients, most products had labeled amounts at or above RDAs. The mean measured content of all ingredients (except thiamin) exceeded labeled amounts (overages). Predicted mean percentage differences exceeded labeled amounts by 1.5-13% for copper, manganese, magnesium, niacin, phosphorus, potassium, folic acid, riboflavin, and vitamins B-12, C, and E, and by ∼25% for selenium and iodine, regardless of labeled amount. In contrast, thiamin, vitamin B-6, calcium, iron, and zinc had linear or quadratic relations between the labeled and percentage differences, with ranges from -6.5% to 8.6%, -3.5% to 21%, 7.1% to 29.3%, -0.5% to 16.4%, and -1.9% to 8.1%, respectively. Analytically adjusted ingredient amounts are linked to adult MVMs reported in the NHANES 2003-2008 via the Dietary Supplement Ingredient Database (http://dsid.usda.nih.gov) to facilitate more accurate intake quantification.
Conclusions: Vitamin and mineral overages were measured in adult MVMs, most of which already meet RDAs. Therefore, nutrient overexposures from supplements combined with typical food intake may have unintended health consequences, although this would require further examination.
Keywords: NHANES; Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA); US Pharmacopeia; dietary supplement; multivitamins; overage; quality control; reference material; sampling plan; upper limit.
© 2017 American Society for Nutrition.
Figures

References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. Centers for disease control and prevention. About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, National Center for Health Statistics. 2014 [cited 2015 Dec 21]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm.
-
- Bailey RL, Gahche JJ, Miller PE, Thomas PR, Dwyer JT. Why US adults use dietary supplements. JAMA Intern Med 2013;173:355–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

