Are neurological complications of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance underestimated?
- PMID: 27974705
- PMCID: PMC5354894
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13861
Are neurological complications of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance underestimated?
Abstract
Objectives: Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is a premalignancy preceding multiple myeloma (MM) or related disorders. Neurological symptoms caused by the monoclonal immunoglobulins or free light-chains are often associated with a high morbidity. We analyzed the prevalence of neuropathy, clinical features and the long-term outcome in 223 patients (pts.) with MGUS.
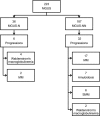
Patients and methods: Between 1/2005 and 3/2015, 223 adult pts. with MGUS were identified in our database.
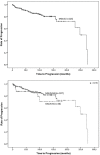
Results: In36/223 pts. (16%) a neuropathy was diagnosed (MGUS associated neuropathy, MGUS-N). 20 pts. (55%) had a distal symmetric axonal neuropathy, 10 pts. (28%) had a chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and 6 pts (17%) a distal acquired demyelinating symmetric polyneuropathy. In MGUS-NN (without neuropathy) and in MGUS-N, progression to smoldering MM, MM or Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia (WM) occurred in 17% of the pts. The Immunoglobulin subtype was predominantly IgG in MGUS-NN and IgM in MGUS-N and ≥5.5% plasma cells in the bone-marrow predicted progression to MM and AL-amyloidosis in MGUS-NN and to WM in MGUS-N (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Due to the substantial prevalence of neuropathies, MGUS pts. should be monitored carefully and referred to a specialized center if neurological symptoms occur.
Keywords: MGUS; MGUS associated neuropathy; monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kyle RA, Durie BG, Rajkumar SV, Landgren O, Blade J, Merlini G, Kroger N, Einsele H, Vesole DH, Dimopoulos M, J San Miguel, Avet-Loiseau H, Hajek R, et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma: IMWG consensus perspectives risk factors for progression and guidelines for monitoring and management. Leukemia. 2010;24:1121–1127. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dispenzieri A, Katzmann JA, Kyle RA, Larson DR, Melton LJ, Colby CL, 3rd, Therneau TM, Clark R, Kumar SK, Bradwell A, Fonseca R, Jelinek DF, Rajkumar SV, et al. Prevalence and risk of progression of light-chain monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: a retrospective population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2010;375:1721–1728. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Group IMW. Criteria for the classification of monoclonal gammopathies, multiple myeloma and related disorders: a report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br J Haematol. 2003;121:749–757. - PubMed
-
- Nobile-Orazio E, Barbieri S, Baldini L, Marmiroli P, Carpo M, Premoselli S, Manfredini E, Scarlato G. Peripheral neuropathy in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: prevalence and immunopathogenetic studies. Acta Neurol Scand. 1992;85:383–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

