Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2+ mammary cancer
- PMID: 27974798
- PMCID: PMC5471138
- DOI: 10.1038/nature20609
Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2+ mammary cancer
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2+ mammary cancer.Nature. 2018 Jan 18;553(7688):366. doi: 10.1038/nature24666. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29236689 Free PMC article.
Abstract
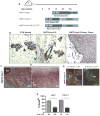
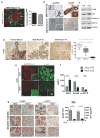
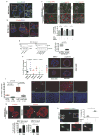
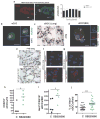
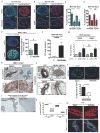
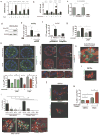
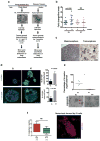
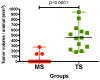
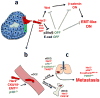
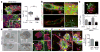
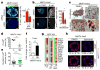
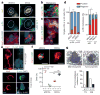
Metastasis is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths; metastatic lesions develop from disseminated cancer cells (DCCs) that can remain dormant. Metastasis-initiating cells are thought to originate from a subpopulation present in progressed, invasive tumours. However, DCCs detected in patients before the manifestation of breast-cancer metastasis contain fewer genetic abnormalities than primary tumours or than DCCs from patients with metastases. These findings, and those in pancreatic cancer and melanoma models, indicate that dissemination might occur during the early stages of tumour evolution. However, the mechanisms that might allow early disseminated cancer cells (eDCCs) to complete all steps of metastasis are unknown. Here we show that, in early lesions in mice and before any apparent primary tumour masses are detected, there is a sub-population of Her2+p-p38lop-Atf2loTwist1hiE-cadlo early cancer cells that is invasive and can spread to target organs. Intra-vital imaging and organoid studies of early lesions showed that Her2+ eDCC precursors invaded locally, intravasated and lodged in target organs. Her2+ eDCCs activated a Wnt-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like dissemination program but without complete loss of the epithelial phenotype, which was reversed by Her2 or Wnt inhibition. Notably, although the majority of eDCCs were Twist1hiE-cadlo and dormant, they eventually initiated metastasis. Our work identifies a mechanism for early dissemination in which Her2 aberrantly activates a program similar to mammary ductal branching that generates eDCCs that are capable of forming metastasis after a dormancy phase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures

Comment on
-
Timing of Metastasis in Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2017 Jun 22;376(25):2486-2488. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcibr1701388. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28636861 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

