Roles of human POLD1 and POLD3 in genome stability
- PMID: 27974823
- PMCID: PMC5156928
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38873
Roles of human POLD1 and POLD3 in genome stability
Abstract
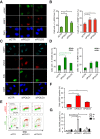
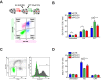
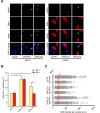
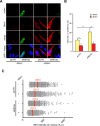
DNA replication is essential for cellular proliferation. If improperly controlled it can constitute a major source of genome instability, frequently associated with cancer and aging. POLD1 is the catalytic subunit and POLD3 is an accessory subunit of the replicative Pol δ polymerase, which also functions in DNA repair, as well as the translesion synthesis polymerase Pol ζ, whose catalytic subunit is REV3L. In cells depleted of POLD1 or POLD3 we found a differential but general increase in genome instability as manifested by DNA breaks, S-phase progression impairment and chromosome abnormalities. Importantly, we showed that both proteins are needed to maintain the proper amount of active replication origins and that POLD3-depletion causes anaphase bridges accumulation. In addition, POLD3-associated DNA damage showed to be dependent on RNA-DNA hybrids pointing toward an additional and specific role of this subunit in genome stability. Interestingly, a similar increase in RNA-DNA hybrids-dependent genome instability was observed in REV3L-depleted cells. Our findings demonstrate a key role of POLD1 and POLD3 in genome stability and S-phase progression revealing RNA-DNA hybrids-dependent effects for POLD3 that might be partly due to its Pol ζ interaction.
Figures


References
-
- Hubscher U., Maga G. & Spadari S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem 71, 133–163 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

