Reconstruction of the Ptotic Breast Using Wise Pattern Skin Deepithelialization
- PMID: 27975010
- PMCID: PMC5142476
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001077
Reconstruction of the Ptotic Breast Using Wise Pattern Skin Deepithelialization
Abstract
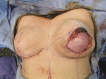
Reconstruction of ptotic or large breasts is challenging due to skin redundancy after skin-sparing mastectomy. Skin reduction can be performed with a long horizontal ellipse, but this often flattens the breast and leaves conspicuous scars medially on the chest. Wise pattern skin reduction is an effective technique for shaping, but excision of skin within the Wise pattern can lead to high rates of skin necrosis and implant exposure or infection. This study describes a technique where the Wise pattern skin is preserved, but deepithelialized, allowing apparent reduction of the skin with preservation of the subdermal plexus. This study reviews data for case series of 26 breasts in 15 patients who have undergone this technique with simultaneous prosthetic reconstruction using an expander.
Figures



References
-
- Breuing KH, Colwell AS. Inferolateral AlloDerm hammock for implant coverage in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2007;59:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Zienowicz RJ, Karacaoglu E. Implant-based breast reconstruction with allograft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120:373–381. - PubMed
-
- Bostwick J. Total mastectomy with breast skin and volume reduction using an inverted ‘T’ incision. In: Bostwick J, editor. In Plastic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery. St Louis: Quality Medical Publisher Inc; 1990. pp. 1048–1054.
-
- Prathap P, Harland RN. Wise pattern mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction. Breast. 2004;13:502–505. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
