Golgi apparatus dis- and reorganizations studied with the aid of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and visualized by 3D-electron tomography
- PMID: 27975144
- PMCID: PMC5359389
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-016-1515-7
Golgi apparatus dis- and reorganizations studied with the aid of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and visualized by 3D-electron tomography
Abstract
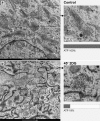
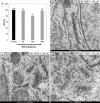
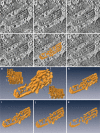
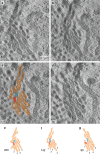
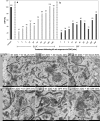
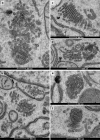
We studied Golgi apparatus disorganizations and reorganizations in human HepG2 hepatoblastoma cells by using the nonmetabolizable glucose analogue 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) and analyzing the changes in Golgi stack architectures by 3D-electron tomography. Golgi stacks remodel in response to 2DG-treatment and are replaced by tubulo-glomerular Golgi bodies, from which mini-Golgi stacks emerge again after removal of 2DG. The Golgi stack changes correlate with the measured ATP-values. Our findings indicate that the classic Golgi stack architecture is impeded, while cells are under the influence of 2DG at constantly low ATP-levels, but the Golgi apparatus is maintained in forms of the Golgi bodies and Golgi stacks can be rebuilt as soon as 2DG is removed. The 3D-electron microscopic results highlight connecting regions that interlink membrane compartments in all phases of Golgi stack reorganizations and show that the compact Golgi bodies mainly consist of continuous intertwined tubules. Connections and continuities point to possible new transport pathways that could substitute for other modes of traffic. The changing architectures visualized in this work reflect Golgi stack dynamics that may be essential for basic cell physiologic and pathologic processes and help to learn, how cells respond to conditions of stress.
Keywords: 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2DG); 3D-electron tomography; Golgi apparatus; Golgi dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The ceramide-enriched trans-Golgi compartments reorganize together with other parts of the Golgi apparatus in response to ATP-depletion.Histochem Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;135(2):159-71. doi: 10.1007/s00418-010-0773-z. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21225431
-
2-Deoxy-D-glucose treatment changes the Golgi apparatus architecture without blocking synthesis of complex lipids.Histochem Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;143(4):369-80. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1297-8. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25422148
-
Viewing Golgi structure and function from a different perspective--insights from electron tomography.Methods Cell Biol. 2013;118:259-79. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-417164-0.00016-1. Methods Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24295312
-
Perspectives on Golgi apparatus form and function.J Electron Microsc Tech. 1991 Jan;17(1):2-14. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060170103. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1991. PMID: 1993935 Review.
-
The Golgi apparatus: defining the identity of Golgi membranes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;17(4):395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.06.013. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15975778 Review.
Cited by
-
The Golgi Apparatus: A Voyage through Time, Structure, Function and Implication in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Cells. 2023 Jul 31;12(15):1972. doi: 10.3390/cells12151972. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Golgin Protein Giantin Regulates Interconnections Between Golgi Stacks.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Aug 27;7:160. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00160. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31544102 Free PMC article.
-
In focus in HCB.Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;147(4):413-414. doi: 10.1007/s00418-017-1552-x. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28285336 No abstract available.
-
Role of the Golgi Apparatus in the Blood-Brain Barrier: Golgi Protection May Be a Targeted Therapy for Neurological Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;55(6):4788-4801. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0691-3. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28730529 Review.
-
Aspergillus nidulans biofilm formation modifies cellular architecture and enables light-activated autophagy.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Jun 1;32(12):1181-1192. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-11-0734. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33826367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger EG (1997) The Golgi apparatus: from discovery to contemporary studies. In: Berger EG, Roth J (eds) The Golgi apparatus. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 1–35. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-8876-9_1
-
- Bergmann M, Schotte H, Lechinsky W. Über die ungesättigten Reduktionsprodukte der Zuckerarten und ihre Umwandlungen, III.: Über 2-desoxyglucose (Glucodesose) Ber Dtsch Chem Ges. 1922;55:158–172. doi: 10.1002/cber.19220550122. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

