Perivascular adipose tissue as a regulator of vascular disease pathogenesis: identifying novel therapeutic targets
- PMID: 27976387
- PMCID: PMC5610156
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13666
Perivascular adipose tissue as a regulator of vascular disease pathogenesis: identifying novel therapeutic targets
Abstract
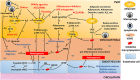
Adipose tissue (AT) is an active endocrine organ with the ability to dynamically secrete a wide range of adipocytokines. Importantly, its secretory profile is altered in various cardiovascular disease states. AT surrounding vessels, or perivascular AT (PVAT), is recognized in particular as an important local regulator of vascular function and dysfunction. Specifically, PVAT has the ability to sense vascular paracrine signals and respond by secreting a variety of vasoactive adipocytokines. Due to the crucial role of PVAT in regulating many aspects of vascular biology, it may constitute a novel therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of vascular disease pathogenesis. Signalling pathways in PVAT, such as those using adiponectin, H2 S, glucagon-like peptide 1 or pro-inflammatory cytokines, are among the potential novel pharmacological therapeutic targets of PVAT.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Perivascular Adipose Tissue - Potential Pharmacological Targets? To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v174.20/issuetoc.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Abe M, Matsuda M, Kobayashi H, Miyata Y, Nakayama Y, Komuro R et al. (2008). Effects of statins on adipose tissue inflammation: their inhibitory effect on MyD88‐independent IRF3/IFN‐beta pathway in macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28: 871–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

