Mycobacterial cell wall biosynthesis: a multifaceted antibiotic target
- PMID: 27976597
- PMCID: PMC5964476
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182016002377
Mycobacterial cell wall biosynthesis: a multifaceted antibiotic target
Abstract
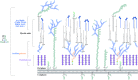
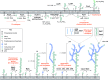
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the etiological agent of tuberculosis (TB), is recognized as a global health emergency as promoted by the World Health Organization. Over 1 million deaths per year, along with the emergence of multi- and extensively-drug resistant strains of Mtb, have triggered intensive research into the pathogenicity and biochemistry of this microorganism, guiding the development of anti-TB chemotherapeutic agents. The essential mycobacterial cell wall, sharing some common features with all bacteria, represents an apparent 'Achilles heel' that has been targeted by TB chemotherapy since the advent of TB treatment. This complex structure composed of three distinct layers, peptidoglycan, arabinogalactan and mycolic acids, is vital in supporting cell growth, virulence and providing a barrier to antibiotics. The fundamental nature of cell wall synthesis and assembly has rendered the mycobacterial cell wall as the most widely exploited target of anti-TB drugs. This review provides an overview of the biosynthesis of the prominent cell wall components, highlighting the inhibitory mechanisms of existing clinical drugs and illustrating the potential of other unexploited enzymes as future drug targets.
Keywords: antibiotics; arabinogalactan; cell wall; mycolic acids; peptidoglycan; tuberculosis.
Figures



References
-
- Abrahams K. A., Cox J. A., Spivey V. L., Loman N. J., Pallen M. J., Constantinidou C., Fernandez R., Alemparte C., Remuinan M. J., Barros D., Ballell L. and Besra G. S. (2012). Identification of novel imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine inhibitors targeting M. tuberculosis QcrB. PLoS ONE 7, e52951. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abrahams K. A., Chung C. W., Ghidelli-Disse S., Rullas J., Rebollo-Lopez M. J., Gurcha S. S., Cox J. A., Mendoza A., Jimenez-Navarro E., Martinez-Martinez M. S., Neu M., Shillings A., Homes P., Argyrou A., Casanueva R., Loman N. J., Moynihan P. J., Lelievre J., Selenski C., Axtman M., Kremer L., Bantscheff M., Angulo-Barturen I., Izquierdo M. C., Cammack N. C., Drewes G., Ballell L., Barros D., Besra G. S. and Bates R. H. (2016). Identification of KasA as the cellular target of an anti-tubercular scaffold. Nature Communications 7, 12581. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alderwick L. J., Radmacher E., Seidel M., Gande R., Hitchen P. G., Morris H. R., Dell A., Sahm H., Eggeling L. and Besra G. S. (2005). Deletion of Cg-emb in corynebacterianeae leads to a novel truncated cell wall arabinogalactan, whereas inactivation of Cg-ubiA results in an arabinan-deficient mutant with a cell wall galactan core. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280, 32362–32371. - PubMed
-
- Alderwick L. J., Seidel M., Sahm H., Besra G. S. and Eggeling L. (2006). Identification of a novel arabinofuranosyltransferase (AftA) involved in cell wall arabinan biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281, 15653–15661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

